General Remote Desktop Connection Remote Desktop (RDP) connections offer the convenience of accessing computers remotely, but occasionally, obstacles may hinder successful connections. This article presents a step-by-step approach to diagnose and resolve common RDP connection problems. Verify RDP Protocol Status: a. On the local computer, check the Remote Desktop settings or Group Policy Objects (GPO)
General Remote Desktop Connection
Remote Desktop (RDP) connections offer the convenience of accessing computers remotely, but occasionally, obstacles may hinder successful connections. This article presents a step-by-step approach to diagnose and resolve common RDP connection problems.
Verify RDP Protocol Status:
a. On the local computer, check the Remote Desktop settings or Group Policy Objects (GPO) to confirm the RDP protocol status. b. For the remote computer, utilize the Registry Editor and a network registry connection to examine and modify the RDP protocol status.
Check RDP Services Status:
a. Ensure that both Remote Desktop Services (TermService) and Remote Desktop Services UserMode Port Redirector (UmRdpService) are operational on both the local and remote computers.
Validate RDP Listener Functionality:
a. Use PowerShell on the affected computer to verify the RDP listener status. b. Address listener issues by exporting and importing the RDP listener configuration from a functioning computer. c. Confirm proper functioning of the RDP listener by examining the permissions of the MachineKeys folder.
Inspect RDP Self-Signed Certificate:
a. Open the Certificates MMC snap-in and remove the RDP self-signed certificate. Subsequently, restart the Remote Desktop Services service and refresh the Certificates snap-in.
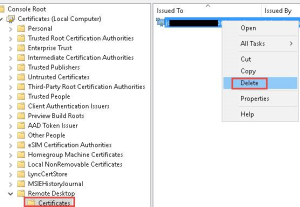
Image by https://learn.microsoft.com/
Verify RDP Listener Port:
a. Employ the Registry Editor to ensure that the RDP listener port is configured to the default port (3389) on both the local and remote computers. b. Prevent conflicts by checking for other applications using the same port.
Check for Firewall Blocking:
a. Employ the psping tool to test connectivity to port 3389 on the affected computer from other computers. b. Collaborate with network administrators to verify that RDP traffic is permitted through the network. c. Investigate firewalls between the source computers and the affected computer to detect any blocking issues.
By diligently applying these troubleshooting methods, you can surmount common RDP connection hurdles and relish uninterrupted remote desktop access. Remember to proceed with caution during each step, considering potential risks before modifying registry settings. Additionally, ensure secure network and firewall configurations to enable seamless RDP connections.
Keep in mind that while remote Desktop’s connections offer valuable remote access capabilities, they must be established and maintained securely to prevent unauthorized access. Always employ robust passwords and activate network-level authentication to bolster security. Through systematic troubleshooting and stringent security measures, you can foster dependable and secure remote desktop connections on your Windows machines.
















Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked with *