Introduction: Kidney stones, scientifically referred to as nephrolithiasis, emerge as a common concern impacting one or both kidneys, predominantly affecting individuals in the age range of 30 to 60. The prevalence is notable, with an estimated 3 in 20 men and up to 2 in 20 women grappling with kidney stones at some juncture in
Introduction:
Kidney stones, scientifically referred to as nephrolithiasis, emerge as a common concern impacting one or both kidneys, predominantly affecting individuals in the age range of 30 to 60. The prevalence is notable, with an estimated 3 in 20 men and up to 2 in 20 women grappling with kidney stones at some juncture in their lifetimes.
Understanding Symptoms:
While some individuals may pass small kidney stones painlessly in their urine, complications may arise when these stones obstruct crucial components of the urinary system, such as the ureter and urethra. This obstruction often manifests as severe abdominal or groin pain and, in more severe cases, can lead to urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Key Symptoms:
- Persistent abdominal or groin pain
- Potential complications leading to UTIs
Deciphering the Causes:
The genesis of kidney stones is intricately tied to the crystallization of waste products within the bloodstream, forming accumulations inside the kidneys over time. Several contributing factors heighten the risk, including insufficient fluid intake, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions altering urine composition.
Contributory Factors:
- Inadequate fluid intake
- Influence of specific medications
- Medical conditions impacting urine composition
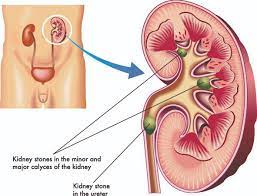
Image by: perthurologyclinic.com.
Navigating the Journey of a Kidney Stone:
Following the formation of a kidney stone, the body initiates efforts to expel it during routine toilet visits. This journey involves traversing the intricate network of kidneys, kidney tubes, and the bladder.
Treatment Modalities and Preventive Strategies:
The approach to managing kidney stones varies based on their size. Smaller stones may be amenable to at-home treatment with medication, while larger stones might necessitate more invasive interventions, such as ultrasound or laser energy. In some instances, surgical procedures, including keyhole surgery, become imperative for the removal of exceptionally large kidney stones.
Strategies for Treatment and Prevention:
- Medication for smaller stones
- Interventional methods for larger stones
- Surgical options for exceptionally large stones
Can Children Get Kidney Stones?
While kidney stones are often associated with adults, they can also affect children. Though less common in the pediatric population, factors such as dehydration, dietary habits, and underlying medical conditions can contribute to the formation of kidney stones in children. Recognizing symptoms early and addressing risk factors is crucial for timely diagnosis and appropriate management in pediatric cases of nephrolithiasis.
I Think I Have a Stone. What do I do?

Image by: ideapod.com
Recurrence Patterns and Proactive Prevention:
A noteworthy statistic suggests that up to half of individuals who have experienced kidney stones may encounter a recurrence within the subsequent 5 years. Consequently, prioritizing hydration emerges as a pivotal aspect of preventive care. Sustaining adequate daily water intake plays a crucial role in maintaining urine dilution, thwarting the formation of waste products into kidney stones.
Proactive Measures for Prevention:
- Consistent daily water intake
- Sustaining clear and diluted urine
In Conclusion:
Comprehending the intricacies of kidney stones involves not only recognizing symptoms and addressing causative factors but also exploring a spectrum of treatment options and adopting proactive measures for prevention. By placing emphasis on hydration and staying informed, individuals can proactively safeguard their kidney health, minimizing the impact of nephrolithiasis on their overall well-being.
















Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked with *