Introduction: Trichotillomania, commonly known as trich, stands as a psychological disorder that delves into the intricate realms of compulsive Hairpulling. This perplexing condition doesn’t discriminate, often finding its roots in the lives of teenagers and young adults. Its impact, however, goes beyond the simple act of pulling hair; it extends its reach to various body
Introduction:
Trichotillomania, commonly known as trich, stands as a psychological disorder that delves into the intricate realms of compulsive Hairpulling. This perplexing condition doesn’t discriminate, often finding its roots in the lives of teenagers and young adults. Its impact, however, goes beyond the simple act of pulling hair; it extends its reach to various body areas, including the head, eyebrows, eyelashes, and even the genital region, creating a web of challenges for those affected.
Symptoms:
Understanding trichotillomania requires a closer examination of its multifaceted symptoms:
- Intense Urge: Individuals grappling with trich feel an irresistible urge to pull out their hair, a compulsion that becomes difficult to resist.
- Tension Build-up: Before succumbing to the urge, there’s a palpable sense of growing tension, creating a psychological struggle.
- Relief After Pulling: The act of pulling out hair is followed by a paradoxical sense of relief, creating a cyclical pattern.
- Triggers: Trich can be triggered by stressful situations, or it may occur unconsciously, adding a layer of unpredictability.
- Bald Patches: The aftermath of trich leaves behind bald patches, each with a unique and sometimes asymmetrical shape, leading to aesthetic concerns.
- Psychological Impact: Beyond the physical manifestations, trich carries a heavy psychological burden, inducing feelings of shame and low self-esteem. Individuals often grapple with the decision to keep their condition concealed, further isolating themselves.
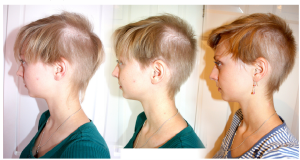
Image by: yendex.com
Causes:
Unraveling the causes of trichotillomania is a complex task, with several factors potentially playing a role:
- Stress Coping Mechanisms: Trich might emerge as a coping mechanism for dealing with stress or anxiety, providing a temporary escape.
- Chemical Imbalances: Drawing parallels with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), trich could be associated with chemical imbalances in the brain.
- Hormonal Changes: The turbulent hormonal changes during puberty might contribute to the onset of trich.
- Addictive Element: For some, hair pulling transcends beyond a habit; it transforms into a form of addiction, intensifying with each episode and further complicating the condition.

Image by: www.freepik.com
When to Seek Help:
Recognizing the signs of trichotillomania is paramount, prompting the need for professional intervention. Consult a General Practitioner (GP) if:
- Hair-pulling behavior is observed in you or your child.
- There’s a habit of eating hair, posing potential health risks.
- Bald patches emerge, necessitating a thorough examination to rule out underlying causes.

Image by: medical dialogues.in
Treatment Approaches:
Addressing trichotillomania involves multifaceted treatment approaches, with cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) taking center stage:
- Identifying Triggers: CBT, specifically habit reversal training, involves meticulous identification of triggers by maintaining a detailed diary of hair-pulling incidents.
- Replacement Strategies: Habit reversal training extends to replacing the act of hair pulling with non-harmful actions, such as utilizing stress balls or fidget toys.
- Emotional Support: The involvement of loved ones becomes crucial, providing emotional support and encouragement throughout the treatment journey.
While antidepressants are generally not the first line of treatment for trich, individual cases may vary, and a tailored approach is often necessary.
Self-Help Strategies:
Empowering individuals dealing with trich, self-help strategies come into play:
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Incorporating deep breathing exercises, soothing baths, and regular exercise as tools to mitigate stress and anxiety.
- Alternative Habits: Creating alternative habits to redirect the urge, such as forming a ball with the fist or wearing tight-fitting accessories, adds a layer of proactive management.
- Communication: Breaking the silence and opening up about trich to trusted individuals can alleviate the anxiety associated with the condition, fostering a sense of understanding and support.
Getting Support:
Acknowledging the intricacies of trichotillomania goes hand in hand with seeking support from organizations like Trichotillomania Support. These platforms offer not only valuable information on treatments and self-help advice but also a sense of community, connecting individuals on a shared journey.
Conclusion:
Trichotillomania, with its nuanced symptoms and intricate causes, requires a holistic approach to management. Through early recognition, professional guidance, self-help strategies, and the support of a community, individuals can navigate the labyrinthine path toward understanding, managing, and ultimately overcoming the challenges posed by this enigmatic disorder.

















Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked with *