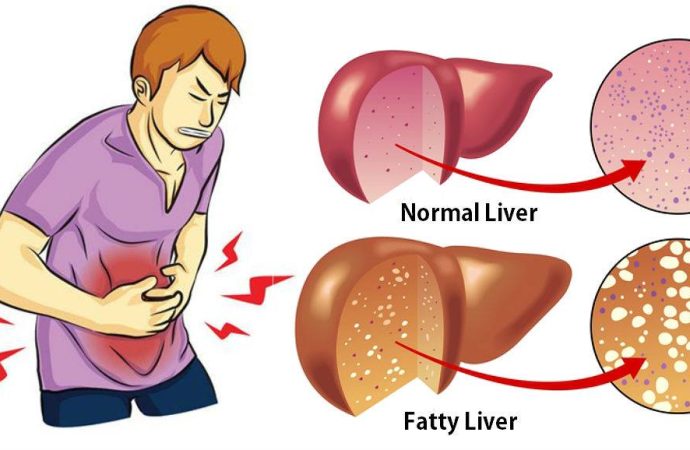
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver cells. It is a growing health concern globally, affecting millions of people of all ages and backgrounds. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention strategies is crucial for managing this condition
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver cells. It is a growing health concern globally, affecting millions of people of all ages and backgrounds. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention strategies is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
What Causes Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver disease can be caused by various factors, including:
- Poor Diet: Consuming a diet high in saturated fats, refined sugars, and processed foods can contribute to the development of fatty liver.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of liver disease as excess fat can accumulate in the liver.
- Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance, often associated with type 2 diabetes, can lead to the accumulation of fat in the liver.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake is a common cause of liver disease, known as alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Medications: Certain medications, including corticosteroids, tamoxifen, and methotrexate, can contribute to the development of liver.
- Genetics: Genetic factors can predispose some individuals to liver disease, even in the absence of other risk factors.

Image by: yendex.com
Recognizing the Symptoms
In its early stages, fatty liver disease may not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, individuals may experience:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Abdominal Pain
- Swelling in the Abdomen
- Jaundice (Yellowing of the Skin and Eyes)
It’s essential to recognize these symptoms and seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosing Fatty Liver
Diagnosing liver disease typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, including:
- Blood Tests: Elevated liver enzymes and other markers may indicate liver inflammation and dysfunction.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans can help visualize fat accumulation in the liver.
- Liver Biopsy: In some cases, a liver biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of liver damage.
Early detection and diagnosis are critical for implementing appropriate treatment and preventing further liver damage.
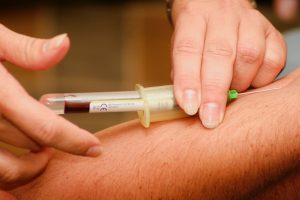
Photo by: unsplash.com
Treatment Options
Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle changes is often the first line of treatment for fatty liver disease. These may include:
- Healthy Diet: Adopting a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce fat accumulation in the liver.
- Weight Loss: Losing excess weight through a combination of diet and exercise can improve liver function and reduce fat in the liver.
- Limiting Alcohol: For individuals with alcoholic liver disease, abstaining from alcohol is essential to prevent further liver damage.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to treat underlying conditions contributing to liver disease, such as insulin resistance or high cholesterol. These medications may include:
- Insulin Sensitizers: Drugs like metformin or pioglitazone can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce fat accumulation in the liver.
- Statins: Cholesterol-lowering medications such as atorvastatin or simvastatin may be prescribed to reduce cholesterol levels and protect the liver.
It’s important to follow the healthcare provider’s recommendations and regularly monitor liver function while taking medications.
Medical Procedures
In advanced cases of fatty liver disease, medical procedures may be necessary to treat complications or remove excess fat from the liver. These may include:
- Liver Transplant: For individuals with severe liver damage or cirrhosis, a liver transplant may be the only treatment option.
- Bariatric Surgery: In obese individuals with fatty liver disease, weight loss surgery may be recommended to reduce the risk of complications and improve liver health.
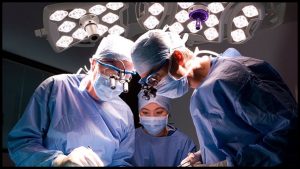
Image by: yendex.com
Prevention Strategies
Preventing fatty liver disease involves adopting a healthy lifestyle and minimizing risk factors. Here are some effective prevention strategies:
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is essential for preventing fatty liver disease. Aim to achieve and maintain a body mass index (BMI) within the healthy range.
Eat a Balanced Diet
Follow a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit consumption of saturated fats, refined sugars, and processed foods.
Limit Alcohol Consumption
If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation. For optimal liver health, men should limit alcohol intake to no more than two drinks per day, while women should limit intake to one drink per day. Explore More About ( Link Between Diabetes or Fast Walking)
Exercise Regularly
Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling, to maintain a healthy weight and promote liver health.
Avoid Smoking
Smoking can increase the risk of liver disease and liver cancer. Quitting smoking can improve overall health and reduce the risk of fatty liver disease.
Get Regular Check-ups
Visit your healthcare provider regularly for routine check-ups and screenings. Early detection and intervention can help prevent the progression of fatty liver disease.
Medications for Fatty Liver Disease
| Medication | Mechanism of Action | Side Effects | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metformin | Improves insulin sensitivity | GI upset, lactic acidosis | Oral, daily dosing |
| Pioglitazone | Improves insulin sensitivity | Weight gain, fluid retention | Oral, daily dosing |
| Atorvastatin | Lowers cholesterol levels | Muscle pain, liver enzyme elevation | Oral, daily dosing |
| Simvastatin | Lowers cholesterol levels | Muscle pain, liver enzyme elevation | Oral, daily dosing |
Conclusion
Fatty liver disease is a common condition that can have serious consequences if left untreated. By understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their liver health effectively. Making lifestyle modifications, seeking medical advice, and following healthcare recommendations are essential for preventing and managing fatty liver disease. With the right approach, individuals can improve liver function, reduce fat accumulation, and lead healthier lives.