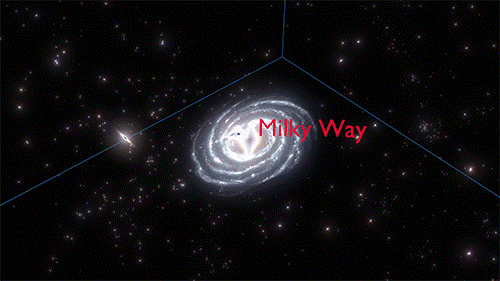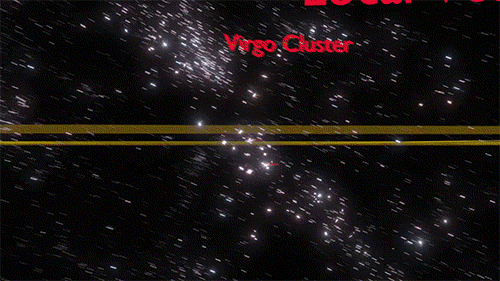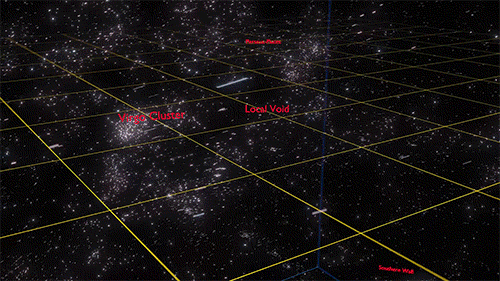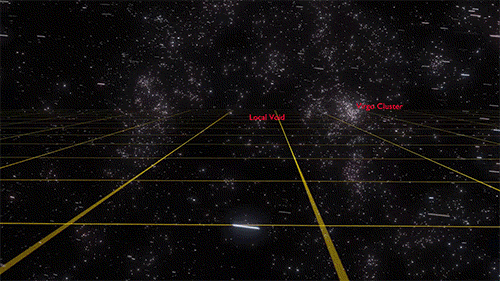
Cosmology, the study of the origin, evolution, and eventual fate of the universe, has captivated human curiosity since ancient times. From the mythical tales of creation to the cutting-edge theories of modern science, the journey of cosmology is as fascinating as the cosmos itself. Ancient Cosmological Myths Origins of the Universe in Mythology Ancient cultures
Cosmology, the study of the origin, evolution, and eventual fate of the universe, has captivated human curiosity since ancient times. From the mythical tales of creation to the cutting-edge theories of modern science, the journey of cosmology is as fascinating as the cosmos itself.
Ancient Cosmological Myths
Origins of the Universe in Mythology
Ancient cultures across the globe developed intricate cosmological myths to explain the creation of the universe. From the Greek myth of Chaos to the Hindu concept of Brahman, these stories reflected humanity’s awe and wonder at the cosmos.
Cosmogony Myths from Different Cultures
The myths of creation vary widely, yet they share common motifs of chaos giving birth to order, gods shaping the cosmos, and the interplay of cosmic forces. These narratives offer insights into early human understanding of the universe.
Early Cosmological Theories
Aristotelian Cosmology
Aristotle proposed a geocentric model of the universe, with Earth at the center surrounded by concentric spheres of celestial bodies. This model dominated Western thought for centuries.
Ptolemaic System
Building upon Aristotle’s ideas, Ptolemy developed a comprehensive geocentric model that accurately predicted the motions of celestial bodies, though it was later superseded by Copernican heliocentrism.
Revolution in Cosmology: Copernicus and Galileo

Image by : Yandex
Heliocentrism vs. Geocentrism
Nicolaus Copernicus challenged the geocentric view with his heliocentric model, placing the Sun at the center of the solar system. Galileo’s telescopic observations provided evidence supporting this revolutionary idea.
Newtonian Universe
Newton’s Laws of Motion and Gravitation
Isaac Newton’s laws of motion and universal gravitation provided a mechanistic framework for understanding celestial dynamics, ushering in the era of Newtonian physics.
Mechanical Universe Paradigm
The universe was viewed as a vast, deterministic machine operating according to Newton’s laws, with celestial bodies following predictable orbits and trajectories.
Einstein’s Revolution: The Theory of Relativity
Special Relativity
Albert Einstein’s theory of special relativity revolutionized physics by showing that space and time are intertwined, with the speed of light as the cosmic speed limit.
General Relativity
General relativity extended these ideas to include gravity as the curvature of spacetime, providing a new understanding of the cosmos on both cosmic and quantum scales.
The Big Bang Theory

Image by : Yandex
Discovery of Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
The serendipitous discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation in 1964 provided compelling evidence for the Big Bang, the prevailing theory of the universe’s origin.
Expansion of the Universe
The Big Bang theory posits that the universe began as a hot, dense singularity and has been expanding ever since, leading to the formation of galaxies and the cosmic web.
Modern Cosmological Theories
Inflationary Cosmology
Inflationary theory proposes a rapid expansion of the universe in the early moments following the Big Bang, resolving some of the puzzles of the standard model.
Multiverse Theory
Multiverse theories speculate about the existence of multiple universes, each with its own physical laws and constants, challenging our notions of cosmic uniqueness.
Dark Matter and Dark Energy
Evidence for Dark Matter
Observational evidence suggests that dark matter, an enigmatic form of matter that does not emit or interact with light, constitutes the majority of the universe’s mass.
Nature of Dark Energy
Dark energy, a mysterious force driving the accelerated expansion of the universe, remains one of the greatest puzzles in modern cosmology, with profound implications for cosmic evolution.
Cosmic Evolution
Formation of Galaxies and Stars
Cosmic evolution traces the formation of galaxies from primordial fluctuations in the early universe, leading to the birth of stars and the formation of planetary systems.
Lifecycle of Stars
Stars evolve through stages of nuclear fusion, eventually culminating in spectacular events such as supernovae, which enrich the cosmos with heavy elements essential for life.
The Fate of the Universe
Big Freeze, Big Crunch, or Big Rip?
The ultimate fate of the universe is a subject of intense debate, with competing theories predicting scenarios ranging from a gradual cooling to a cataclysmic collapse or rip.
Implications of Cosmological Models
Each cosmological model carries profound implications for the future of the universe and the possibility of life’s persistence, raising existential questions about our place in the cosmos.
Search for Extraterrestrial Life
Drake Equation
The Drake Equation provides a framework for estimating the number of extraterrestrial civilizations in the Milky Way galaxy, highlighting the tantalizing possibility of cosmic companionship.
Fermi Paradox
Despite the potential abundance of habitable worlds, the Fermi Paradox questions why we have yet to encounter evidence of extraterrestrial intelligence, fueling speculation and debate.
Cosmology and Philosophy
Cosmic Fine-Tuning
The remarkable fine-tuning of the universe’s constants and parameters has led to philosophical debates about the existence of a cosmic designer or the implications of a multiverse.
Cosmic Meaning and Purpose
Cosmology raises existential questions about the nature of existence, the origins of consciousness, and humanity’s place in the grand tapestry of the cosmos, inspiring both awe and introspection.
Cosmology in Popular Culture
Cosmic Themes in Literature and Film
From epic sagas to mind-bending science fiction, cosmological themes pervade popular culture, reflecting humanity’s fascination with the cosmos and its mysteries.
Influence on Society
Cosmological discoveries and theories have profound impacts on society, shaping our worldview, inspiring technological advancements, and fostering a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of all things.
Conclusion
From ancient myths to modern theories, the journey of cosmology is a testament to human curiosity, ingenuity, and imagination. As we peer into the depths of space and time, we continue to unravel the mysteries of the cosmos, forging new connections between science, philosophy, and culture.
FAQs
Is the Big Bang theory proven?
While the Big Bang theory is supported by extensive evidence, including the cosmic microwave background radiation, it remains a scientific theory subject to refinement and revision.
What is dark matter?
Dark matter is a hypothetical form of matter that does not emit or interact with electromagnetic radiation, yet exerts gravitational influence on visible matter, accounting for the observed dynamics of galaxies and galaxy clusters.
Are there other universes besides our own?
Multiverse theories suggest the possibility of parallel universes with different physical laws and constants, although direct empirical evidence remains elusive.
What caused the Big Bang?
The cause of the Big Bang remains a subject of speculation, with some theories positing a quantum fluctuation or a pre-existing state of the universe beyond our current understanding.
How does cosmology relate to philosophy?
Cosmology addresses fundamental questions about the nature of reality, the origins of the universe, and the existence of life, intersecting with philosophical inquiries into existence, consciousness, and the human condition.