The Future of Biometric Authentication Technologies As digital security continues to evolve, biometric authentication technologies have become central to safeguarding online activities, securing physical spaces, and enhancing user convenience. Biometric authentication refers to systems that use unique physical or behavioral traits to verify identity. In the past few decades, we’ve witnessed remarkable advancements in biometric
The Future of Biometric Authentication Technologies
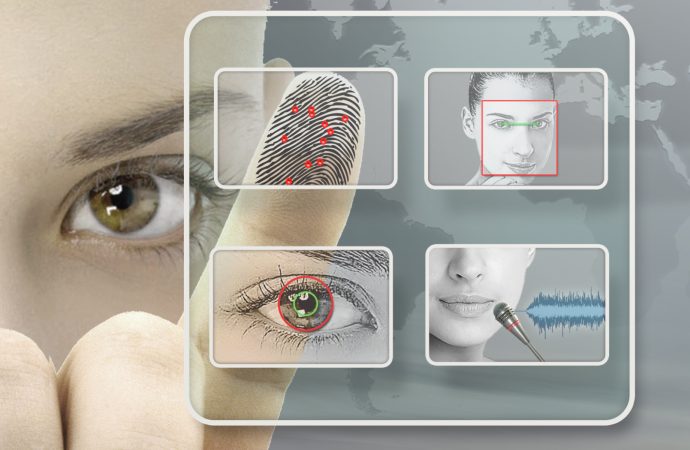
As digital security continues to evolve, biometric authentication technologies have become central to safeguarding online activities, securing physical spaces, and enhancing user convenience. Biometric authentication refers to systems that use unique physical or behavioral traits to verify identity. In the past few decades, we’ve witnessed remarkable advancements in biometric technologies, which promise to revolutionize the way we secure access to our devices, data, and facilities. This article explores the latest trends, benefits, examples, case studies, and future directions of biometric authentication.
Introduction to Biometric Authentication

Image by Yandex.com
Biometric authentication systems leverage physical and behavioral characteristics, such as fingerprints, iris scans, voice recognition, and facial features, to confirm an individual’s identity. With the rise of cybercrime and the need for stronger security, biometric authentication is rapidly gaining favor over traditional methods like passwords and PINs.
The global market for biometric authentication is expected to grow significantly, as it offers both increased security and improved user experience. This growth is driven by its seamless integration into smartphones, financial services, healthcare, and even government services.
Behavioral Biometrics: Eye Movement and Brainwave Authentication
The most recent developments in biometric technology are in the realm of behavioral biometrics, where the focus has shifted from physical traits to unique patterns of human behavior.
Eye movement and brainwave-based authentication are two exciting innovations that are gaining attention. Eye movement biometrics track how a person’s eyes move, their blinking patterns, and how they gaze at certain objects. Researchers are also exploring brainwave patterns as an authentication tool. Since brainwave patterns are unique to each individual, they present a potentially secure method for identification.
A recent study in 2024 assessed the feasibility of using eye movements and brainwave patterns for authentication. It found that these systems provided high usability scores and demonstrated strong potential for real-world application. However, concerns regarding privacy and the cognitive effort involved in brainwave authentication were noted. Despite these challenges, this method represents a major step toward more secure and less intrusive biometric solutions.
Example:
Eye-tracking technology is already being used in research environments to monitor user behavior, and it could soon be integrated into mobile devices or smart glasses for hands-free authentication.
Biometric Tokenization: Enhancing Privacy
With increasing concerns about privacy and the security of biometric data, biometric tokenization is gaining traction as an effective way to mitigate these risks.
Biometric tokenization involves converting sensitive biometric information into a non-sensitive token, which is stored securely. When the user’s biometric data is required for authentication, the system compares the token instead of the raw data. This ensures that even if data is breached, it cannot be used for malicious purposes. By combining tokenization with public-key cryptography, biometric authentication systems can achieve a high level of security while minimizing the risk of data exposure.
Case Study:
For instance, companies like HyTrust and Gemalto have integrated tokenization into their biometric systems, enabling businesses to authenticate employees without directly storing biometric data. This method is particularly valuable in industries like finance and healthcare, where data breaches could lead to severe consequences.
Continuous and Non-Intrusive Authentication
One of the biggest challenges of traditional biometric authentication methods is that they require users to perform a specific action, such as scanning a fingerprint or face. However, continuous and non-intrusive authentication aims to provide a seamless security solution that does not disrupt the user’s experience.
This approach continuously monitors the user’s biometrics without requiring any additional input. It is particularly useful in virtual environments such as the Metaverse, where security needs to be constantly maintained in a dynamic, immersive environment.
The concept of continuous authentication is already being implemented in mobile devices, where biometric systems continually check for signs of user presence. For example, if a person’s gaze shifts away from their device for too long, the system could automatically lock the device, ensuring that no unauthorized user gains access.
Example:
Apple’s Face ID system is an example of continuous authentication on mobile devices. It continuously monitors the user’s face while the device is in use, ensuring that only the authorized user can access the phone.
Innovations in Biometric Modalities

Image by Yandex.com
While fingerprint and facial recognition are the most well-known biometric modalities, there are new innovations that are transforming the landscape. For instance, palm vein recognition is an emerging technology that scans the veins in the palm to verify identity.
Palm vein authentication has several advantages over traditional fingerprint scanning, including its difficulty to replicate and its less intrusive nature. For example, Tencent’s Weixin Palm Payment system, implemented in China, allows users to authenticate payments by scanning their palms. This contactless method enhances security and convenience, making it ideal for high-traffic locations like retail stores and transportation hubs.
Case Study:
At airports in Japan and China, palm vein authentication has been implemented to streamline passenger check-ins and security screening. Passengers can quickly verify their identity by scanning their palm, reducing the time spent at traditional check-in counters and improving overall airport efficiency.
Consumer Device Integration: Iris Scanning and Beyond
As biometric technologies advance, their integration into everyday consumer devices has become more prevalent. One notable example is iris scanning, which uses the unique patterns in the iris to authenticate individuals.
In 2024, Apple’s Vision Pro headset integrated iris scanning technology to authenticate users. This technology not only adds a layer of security but also enhances user convenience, as it eliminates the need to remember passwords or PINs. By incorporating biometric authentication into such devices, companies are making it easier for users to securely access their personal data without compromising security.
Example:
Samsung’s Galaxy S10 includes an iris scanner that can be used to unlock the phone or make secure payments, adding an extra layer of security on top of traditional fingerprint scanning and facial recognition.
The Future of Biometric Authentication
The future of biometric authentication is poised for significant growth, especially with the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies will enable biometric systems to become more accurate and efficient over time, allowing for faster processing and higher levels of security.
One area to watch is the integration of biometrics into the Internet of Things (IoT). As smart homes, smart cars, and wearables become more common, biometric authentication will play a key role in ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to these devices.
Additionally, biometric authentication will continue to evolve with the development of multi-modal authentication systems, which combine several biometric traits (e.g., facial recognition and voice recognition) for even greater security.
Privacy Concerns and Ethical Implications
Despite the advancements in biometric authentication, there are significant privacy and ethical concerns associated with its use. Biometric data is highly sensitive, and its collection raises the risk of data breaches and misuse. The potential for biometric information to be stolen or used without consent is a major concern, particularly in countries where data protection laws are not as robust.
The ethical implications of collecting biometric data also raise questions about consent, surveillance, and the potential for discrimination. For example, facial recognition systems have been criticized for their potential to perpetuate biases, particularly in systems that may misidentify individuals based on race or gender.
Regulations and Standards in Biometric Authentication

Image by Yandex.com
To address these concerns, governments and organizations are working to establish regulations and standards for the use of biometric data. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, for example, includes specific provisions regarding the use of biometric data, requiring explicit consent and ensuring that data is securely stored and processed.
Additionally, international standards bodies are working to develop frameworks for the interoperability and security of biometric authentication systems. These standards are critical to ensuring that biometric systems are both effective and ethically sound.
Conclusion:
As biometric authentication technologies continue to evolve, there will be increasing pressure to balance innovation with privacy and security concerns. The future of these technologies holds great promise, offering enhanced security, greater user convenience, and broader applications across industries. However, developers and policymakers must work together to ensure that these advancements do not compromise individual privacy or ethical standards.
Ultimately, the success of biometric authentication will depend on the ability to create systems that are both secure and user-friendly, while addressing the critical concerns of privacy and ethical responsibility. As biometric authentication continues to mature, we can expect a future where digital security is not only more robust but also seamlessly integrated into our daily lives.