This article is designed for technology enthusiasts, PC gamers, and those interested in understanding the latest developments in CPU technology. It caters to individuals seeking detailed insights into Intel’s new Alder Lake chips, specifically the concept of E-cores and P-cores, and how they contribute to enhanced performance and efficiency. Introduction to Intel’s E-Cores and P-Cores
This article is designed for technology enthusiasts, PC gamers, and those interested in understanding the latest developments in CPU technology. It caters to individuals seeking detailed insights into Intel’s new Alder Lake chips, specifically the concept of E-cores and P-cores, and how they contribute to enhanced performance and efficiency.
Introduction to Intel’s E-Cores and P-Cores
In the ever-evolving landscape of CPU technology, Intel’s latest innovation, the Alder Lake chips, has taken center stage. At the heart of this advancement lies a distinctive architectural approach: the incorporation of two types of CPU cores known as E-Cores and P-Cores. This revolutionary concept brings a new dimension to the way CPUs function, promising enhanced performance and efficiency like never before. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of Intel’s E-Cores and P-Cores, understanding their roles, benefits, and the significant impact they have on redefining the world of CPU architecture.
Why the Evolution in Intel CPUs?
Before we dive into the specifics of E-Cores and P-Cores, let’s revisit the journey of CPU core evolution. From the era of single-core CPUs to the introduction of multi-core setups and multithreading, the goal has always been to maximize computational power while maintaining efficiency. However, Intel’s recent introduction of two distinct core types within a single CPU package marks a significant departure from conventional designs. This innovative approach draws inspiration from ARM’s big.LITTLE architecture, which leverages different core types to achieve a balance between performance and energy consumption.

Image by:https://www.intel.com/
Deciphering Intel P-Cores: Power and Performance
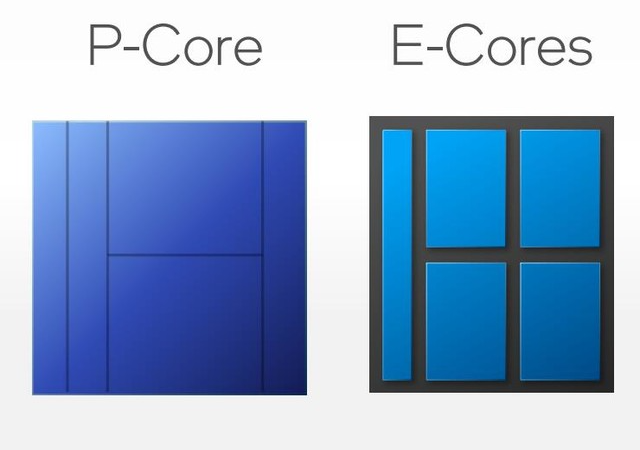
P-Cores, short for performance cores, emerge as the powerhouses within Intel’s Alder Lake CPUs. These cores exhibit remarkable processing capacity, operating at high clock speeds and excelling in tackling intensive tasks. Equipped with Intel’s cutting-edge Golden Cove or Raptor Cove microarchitecture, P-Cores take on the heavy lifting, driving optimal single-core performance. Furthermore, the inclusion of hyperthreading empowers each P-Core to handle two processing threads simultaneously. This performance-oriented design is a game-changer for tasks demanding substantial computational prowess.

Image by:https://helpdeskgeek.com/
Exploring Intel E-Cores: Efficiency and Optimization
In contrast to the prowess of P-Cores, E-Cores, or efficiency cores, bring a different set of capabilities to the table. These cores prioritize power efficiency and excel in tasks that require multitasking and background processing. Despite being smaller and less powerful than their P-Core counterparts, E-Cores shine in their ability to consume less energy while still delivering commendable performance. Based on Intel’s Gracemont microarchitecture, E-Cores form a crucial part of the dual-core configuration, collaborating seamlessly with P-Cores to optimize overall CPU performance.

Image by:https://www.techpowerup.com/
The Symbiotic Relationship: P-Cores and E-Cores Together
The real magic happens when P-Cores and E-Cores join forces in a symbiotic relationship. This harmony between high-performance P-Cores and efficient E-Cores results in a versatile CPU architecture capable of handling a wide array of tasks. Whether it’s resource-intensive gaming or everyday multitasking, the combined efforts of these core types ensure an optimal balance between raw power and energy conservation. The coexistence of P-Cores and E-Cores paves the way for a new era in CPU technology, offering users the best of both worlds.
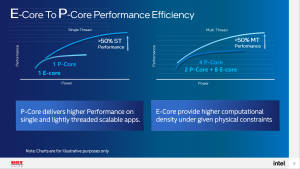
Image by:https://www.velocitymicro.com/
The Impressive Results and Future Outlook
The introduction of E-Cores and P-Cores within Intel’s Alder Lake CPUs has yielded remarkable results, as evidenced by performance benchmarks. The 12th-Gen chips boast a 19% improvement in performance compared to their 11th-Gen counterparts, while the 13th-Gen chips build upon this success. Even more striking is the 40% performance enhancement of E-Cores over previous generations, showcasing their prowess in optimizing efficiency. This hybrid core layout not only caters to gamers seeking high-performance experiences but also meets the demands of productivity-focused tasks. As the tech landscape evolves, this novel approach to CPU architecture paves the way for even greater innovations in the future.
Conclusion: Embracing a New Era of CPU Innovation
Intel’s E-Cores and P-Cores signify a monumental leap in CPU technology, introducing a paradigm shift in how cores collaborate within a single package. The fusion of performance-centric P-Cores with efficiency-driven E-Cores ushers in a new era of versatility and capability. As other tech giants consider similar hybrid approaches, Intel has emerged as a trailblazer in redefining the boundaries of CPU architecture. This innovation not only benefits gamers and professionals but also propels the entire industry toward a future where performance and efficiency coexist harmoniously. With E-Cores and P-Cores, Intel beckons us to embrace a new dawn of CPU innovation and the endless possibilities it holds.
















Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked with *