Introduction: Wounds are a common occurrence in our daily lives, whether from minor accidents or unforeseen incidents. Proper care is essential not only for preventing infections but also for expediting the body’s natural healing process. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of basic wound care, providing a detailed roadmap for individuals seeking effective strategies
Introduction:
Wounds are a common occurrence in our daily lives, whether from minor accidents or unforeseen incidents. Proper care is essential not only for preventing infections but also for expediting the body’s natural healing process. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of basic wound care, providing a detailed roadmap for individuals seeking effective strategies for wound management and swift recovery.
Immediate Treatment
The initial moments after sustaining a wound are critical for preventing complications. Follow these steps for immediate treatment:
- Cleaning with Water and Mild Soap: Wash the wound thoroughly with clean water and mild soap to remove any impurities. This step helps reduce the risk of infection.
- Gentle Pressure to Stop Bleeding: Apply gentle pressure to the wound to control bleeding. This can be achieved by using a clean cloth or sterile gauze.
- Burn Wounds: For burn wounds, run cool water over the affected area or apply a cool, wet cloth. It’s crucial not to pop or drain blisters that may form.
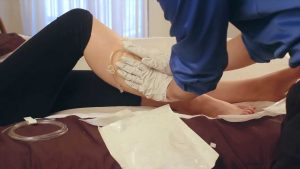
Image by: yendex.com
Antibiotic Ointment and Bandaging
Once the immediate treatment is administered, the next steps involve applying antibiotic ointment and bandaging the wound:
- Bacitracin Antibiotic Ointment or White Petroleum: Apply a thin layer of bacitracin antibiotic ointment or white petroleum to the wound. These substances act as protective barriers, preventing infection and aiding in the healing process.
- Bandaging: Cover the treated wound with a sterile bandage. This helps keep the wound clean and protected from external contaminants.
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the wound area twice daily with soap and water. After each cleaning, apply a new layer of antibiotic ointment and re-bandage the wound. It’s important to note that the use of hydrogen peroxide or alcohol for wound cleaning is discouraged, as these substances may impede the healing process.
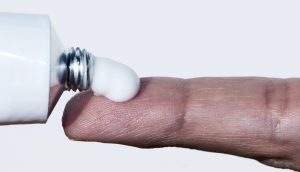
Image by: yendex.com
Special Care for Deep Wounds
While basic wound care suffices for many injuries, deep or gaping wounds may require additional attention:
- Stitches or Professional Medical Attention: Seek medical advice for deep wounds. Some may necessitate stitches or specific wound care procedures administered by a healthcare professional.
- Bite Injuries: Certain bite injuries, such as those from animals, may require special care beyond standard first aid measures. Prompt medical attention is crucial to address potential complications. Treatment for other Health Problems
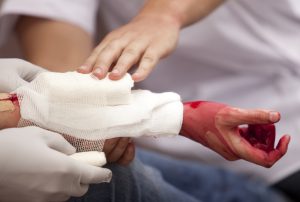
Image by: yendex.com
Tetanus Immunization
Tetanus is a serious infection that can arise from skin injuries, making immunization an integral aspect of wound care:
- Vaccination Schedule: Ensure you have received the recommended series of three tetanus vaccinations during infancy. Additionally, adults should receive a booster shot every 10 years.
- Special Considerations: In some cases, especially with puncture wounds or those exposed to dirt, a tetanus booster may be required if it has been more than five years since the last vaccination.
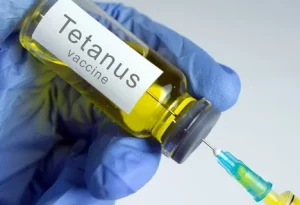
Image by: yendex.com
Basic Wound Care Products
Here’s a breakdown of various wound care products, highlighting their applications, pros, and cons:
| Product | Application | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacitracin Antibiotic Ointment | Apply to clean wounds | Prevents infection, aids healing | Allergic reactions in some individuals |
| White Petroleum | Wound coverage | Creates a protective barrier | May feel greasy; not suitable for all |
| Hydrogen Peroxide | Not recommended for use | Was traditionally used, but may hinder healing | Can damage healthy cells; not advised |
| Alcohol | Not recommended for use | Used less due to skin irritation | Slows healing, causes dryness |
Conclusion:
In conclusion, mastering the basics of wound care is an invaluable skill that can contribute significantly to a smooth recovery process. From immediate treatment to long-term care, following these guidelines promotes healing, reduces infection risks, and ensures optimal outcomes. However, it’s essential to recognize the limitations of basic wound care and seek professional medical attention for severe injuries or situations that demand specialized treatment. By understanding and implementing these fundamental wound care principles, individuals can take proactive steps towards safeguarding their health and well-being.
















