Understanding Concussions: A Primer Concussion are a type of traumatic brain injury (TBI) that occur when a blow or jolt to the head disrupts normal brain function. They can happen to anyone, from athletes engaged in high-impact sports to individuals involved in everyday activities like driving or even slipping and falling. While concussions are often
Understanding Concussions: A Primer
Concussion are a type of traumatic brain injury (TBI) that occur when a blow or jolt to the head disrupts normal brain function. They can happen to anyone, from athletes engaged in high-impact sports to individuals involved in everyday activities like driving or even slipping and falling. While concussions are often associated with sports injuries, they can occur in various settings and circumstances. Explore your Health About (Warning Signs of Dangerous Health Conditions)
Causes of Concussions
Concussions typically result from a sudden acceleration or deceleration of the head, causing the brain to move within the skull rapidly. This movement can lead to the stretching and damaging of brain cells, triggering a range of symptoms. Common causes of concussions include:
- Sports injuries (e.g., football, soccer, hockey)
- Motor vehicle accidents
- Falls
- Physical altercations or assaults
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
Identifying a concussion is crucial for seeking appropriate medical attention and preventing further injury. While symptoms may vary from person to person, there are several common signs to watch for:
Physical Symptoms
- Headache or pressure in the head
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness or loss of balance
- Sensitivity to light or noise
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue or drowsiness
Cognitive Symptoms
- Confusion or feeling “foggy”
- Difficulty concentrating or remembering
- Slurred speech
- Delayed response to questions
Emotional Symptoms
- Irritability or mood swings
- Anxiety or depression
- Changes in sleep patterns
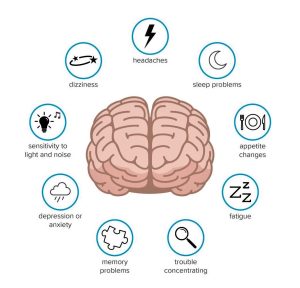
Image by: yendex.com
Steps to Take if You Suspect a Concussion
If you or someone else experiences a blow to the head or body and exhibits signs of a concussion, it’s essential to take immediate action. Follow these steps:
- Seek Medical Attention: Even if symptoms seem mild, it’s crucial to see a healthcare professional for an evaluation. They can assess the severity of the injury and recommend appropriate treatment.
- Rest and Recovery: Limit physical and cognitive activities to allow the brain time to heal. This may involve taking time off work or school and avoiding activities that could exacerbate symptoms.
- Follow Medical Advice: Follow the healthcare provider’s instructions for recovery, which may include resting, avoiding screens and bright lights, and gradually returning to normal activities.
- Monitor Symptoms: Keep track of any changes or worsening of symptoms and report them to your healthcare provider.
Long-Term Effects and Complications
While many people recover fully from concussions with proper rest and medical care, some may experience persistent symptoms or complications. These can include:
- Post-concussion syndrome: Persistent symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and cognitive difficulties that last for weeks or months.
- Second impact syndrome: A rare but potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when a person sustains a second concussion before fully recovering from the first.
- Cognitive issues: Some individuals may experience long-term cognitive impairments, such as memory problems or difficulty concentrating.
Prevention Strategies
While it’s not always possible to prevent concussions entirely, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk:
- Wear appropriate safety gear during sports and recreational activities, including helmets and mouthguards.
- Follow safety guidelines and rules in sports and recreational activities.
- Avoid risky behaviors that increase the likelihood of falls or accidents, such as drinking and driving or engaging in physical altercations.

Image by: yendex.com
Concussion Recognition and Management
| Symptoms | Concussion | Other Head Injuries |
|---|---|---|
| Headache | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Nausea/Vomiting | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Dizziness | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Sensitivity to Light/Noise | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Blurred Vision | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Cognitive Issues | ✔️ | Depends |
| Emotional Changes | ✔️ | Depends |
| Loss of Consciousness | Sometimes | Sometimes |
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs of a concussion is essential for prompt diagnosis and treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and steps to take if a concussion is suspected, individuals can protect their brain health and minimize the risk of long-term complications. If you suspect you or someone else has sustained a concussion, don’t hesitate to seek medical attention and follow appropriate care guidelines.
















