Understanding the Complexity of Tinnitus Tinnitus, often described as “ear ringing,” is a common auditory phenomenon that affects millions of people worldwide. While it manifests as a ringing sensation in the ears for many, its forms and intensities can vary widely among individuals. Those experiencing worsening symptoms often find themselves seeking answers and solutions to
Understanding the Complexity of Tinnitus
Tinnitus, often described as “ear ringing,” is a common auditory phenomenon that affects millions of people worldwide. While it manifests as a ringing sensation in the ears for many, its forms and intensities can vary widely among individuals. Those experiencing worsening symptoms often find themselves seeking answers and solutions to alleviate their discomfort. But what exactly triggers the exacerbation of tinnitus? Let’s delve into the intricacies of this condition to shed light on the factors that contribute to its worsening.
Potential Causes of Worsening Tinnitus
1. Exposure to Loud Noise
Prolonged exposure to loud noises is a well-known risk factor for tinnitus. Individuals working in noisy environments or frequenting loud events without adequate hearing protection are particularly susceptible. The continued assault on the delicate structures of the inner ear can lead to heightened tinnitus symptoms over time.
2. Stress and Anxiety
The connection between stress, anxiety, and tinnitus exacerbation is well-documented. Elevated stress levels can exacerbate existing tinnitus or even trigger its onset in susceptible individuals. The body’s physiological response to stress can amplify the perception of ear ringing, making it seem more pronounced and distressing.
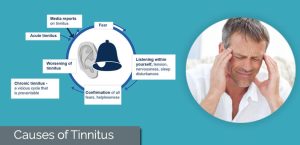
Image by: yendex.com
3. Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can exacerbate tinnitus symptoms. These may include:
a. Hearing Loss:
Age-related hearing loss or noise-induced hearing loss can exacerbate tinnitus symptoms due to the reduced ability of the auditory system to process sound properly.
b. Temporal Mandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders:
Dysfunction of the TMJ, which connects the jawbone to the skull, can lead to referred ear symptoms, including tinnitus.
c. Meniere’s Disease:
This inner ear disorder characterized by vertigo, hearing loss, and tinnitus can cause fluctuating and worsening symptoms over time.
Image by: yendex.com
4. Medications and Substances
Certain medications and substances have been linked to tinnitus exacerbation as a side effect. These may include:
- Ototoxic Drugs: Certain medications, such as some antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, and high doses of aspirin, can damage the inner ear and worsen tinnitus symptoms.
- Caffeine and Nicotine: Stimulants like caffeine and nicotine can exacerbate tinnitus in some individuals by increasing blood pressure and constricting blood vessels, affecting blood flow to the ears.
5. Poor Sleep Quality
Inadequate sleep or disrupted sleep patterns can contribute to tinnitus worsening. Sleep deprivation can heighten stress levels and exacerbate the perception of ear ringing, creating a vicious cycle of sleep disturbances and increased tinnitus severity.

Image by: sleepdoctor.com
Managing and Alleviating Worsening Tinnitus
While the factors contributing to worsening tinnitus can be multifaceted and complex, there are strategies individuals can employ to manage and alleviate their symptoms:
1. Hearing Protection
Avoiding exposure to loud noises and using ear protection devices, such as earplugs or earmuffs, can prevent further damage to the auditory system and mitigate tinnitus exacerbation.
2. Stress Management
Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in relaxing activities can help alleviate the impact of stress on tinnitus symptoms.
3. Seeking Medical Evaluation
Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as an audiologist or an otolaryngologist, is essential for identifying and addressing any underlying medical conditions contributing to tinnitus worsening. They can provide personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs.
4. Medication Review
Reviewing medications with a healthcare provider to identify and potentially substitute ototoxic drugs can help minimize tinnitus exacerbation. Explore more About (Ankle Sprain)
5. Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate hydration, and limiting caffeine and nicotine intake, can contribute to overall well-being and may alleviate tinnitus symptoms.
6. Sound Therapy
Utilizing sound therapy techniques, such as white noise machines, soothing music, or specialized hearing aids that emit masking sounds, can help distract from and reduce the perception of tinnitus.
Common Triggers of Worsening Tinnitus
| Triggers | Description |
|---|---|
| Loud Noise Exposure | Prolonged exposure to loud noises can exacerbate tinnitus symptoms over time. |
| Stress and Anxiety | Elevated stress levels can amplify the perception of ear ringing. |
| Underlying Medical Conditions | Conditions such as hearing loss, TMJ disorders, and Meniere’s disease can worsen tinnitus. |
| Medications and Substances | Certain drugs and substances, including ototoxic medications, caffeine, and nicotine, may worsen tinnitus symptoms. |
| Poor Sleep Quality | Inadequate sleep patterns can contribute to heightened tinnitus severity. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the worsening of tinnitus can result from a combination of factors, including exposure to loud noise, stress and anxiety, underlying medical conditions, medications, poor sleep quality, and more. Understanding these potential triggers is crucial for individuals seeking relief from their symptoms. By implementing strategies such as hearing protection, stress management, seeking medical evaluation, medication review, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and utilizing sound therapy, individuals can take proactive steps to manage and alleviate the worsening of tinnitus. Remember, addressing tinnitus requires a comprehensive approach tailored to individual needs, and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals is paramount in navigating this condition effectively.
















