Introduction The world beneath our feet is a complex network of pipes, cables, tunnels, and conduits. As cities grow and infrastructure projects become more advanced, the need to understand this hidden landscape is more important than ever. That’s where underground utility mapping comes into play. Underground utility mapping helps identify and document the location of
Introduction
The world beneath our feet is a complex network of pipes, cables, tunnels, and conduits. As cities grow and infrastructure projects become more advanced, the need to understand this hidden landscape is more important than ever. That’s where underground utility mapping comes into play.
Underground utility mapping helps identify and document the location of buried infrastructure such as water lines, gas pipes, power cables, and fiber optics. This information is crucial for construction, maintenance, and urban planning projects. Without proper mapping, digging into the ground can lead to accidents, service disruptions, or costly delays.
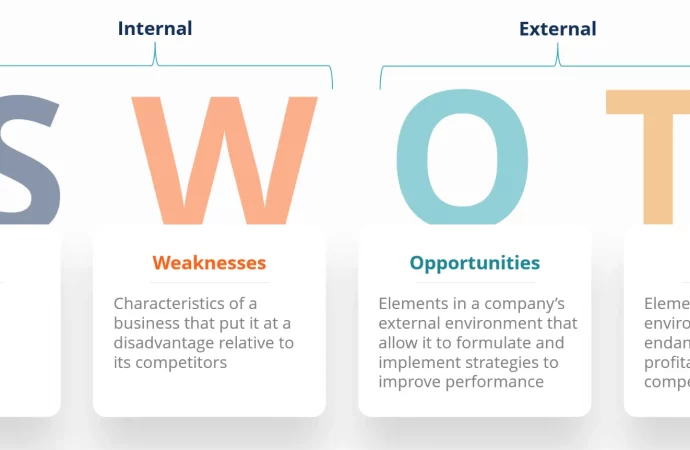
With the global push toward smarter cities and advanced infrastructure, the underground utility mapping industry is set to experience significant growth by 2032. In this article, we will explore the SWOT analysis of this evolving market—highlighting its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Understanding Underground Utility Mapping
Underground utility mapping involves using advanced tools and technologies to detect and visualize buried utilities without the need for excavation. Common methods include:
- Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
- Electromagnetic location
- LiDAR
- GPS and Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
- Acoustic and thermal sensors
These technologies help construction companies, utility providers, and city planners avoid damaging infrastructure while saving time and money.
Strengths of the Underground Utility Mapping Market
Accuracy and Safety
Modern underground mapping tools offer high levels of accuracy, allowing teams to detect the exact location and depth of buried utilities. This reduces the risk of damaging essential services and improves worker safety during excavation.
Growing Urbanization
As more people move to cities, there is an increasing need to upgrade and expand underground infrastructure. Utility mapping ensures these developments happen efficiently and without disruption.
Regulatory Support
Governments around the world are encouraging safe digging practices. In many countries, laws require utility locating before excavation. This boosts demand for underground mapping services.
Integration with Smart Cities
Underground utility data is a critical component of smart city planning. Cities are now integrating this data with GIS platforms to manage resources and respond to emergencies more effectively.
Weaknesses in the Market
High Cost of Equipment and Services
Advanced utility mapping technologies can be expensive to purchase and maintain. This can be a barrier for smaller companies or municipalities with limited budgets.
Skill Shortages
Operating underground mapping tools requires training and expertise. There is currently a lack of skilled professionals who can accurately interpret and apply the data collected.
Inconsistent Data Quality
In many regions, older infrastructure was installed without accurate records. This leads to gaps in existing data and can affect the accuracy of new mapping efforts.
Limited Access in Dense Areas
In heavily built-up environments, it can be challenging to use large equipment or get clear signals from sensors. Buildings and other structures may interfere with mapping tools.
Opportunities for Growth
Advancements in Technology
The development of more portable, affordable, and user-friendly tools is opening up the market. Drones equipped with scanning technology and AI-driven data analysis are making mapping easier and faster.
Infrastructure Modernization
Across the globe, governments are investing in infrastructure upgrades. Utility mapping is a key step in planning and executing these projects, especially in water, energy, and telecommunications.
Rising Demand in Emerging Markets
Developing countries are catching up on urban planning and infrastructure development. These regions offer vast opportunities for utility mapping companies looking to expand.
Environmental and Disaster Management
Accurate underground maps can help cities prepare for natural disasters such as floods and earthquakes by locating vulnerable infrastructure. This also aids in quick response and recovery.
Integration with Building Information Modeling (BIM)
As BIM becomes more widely used in construction, incorporating underground utility data into 3D models improves planning and reduces conflicts during building projects.
Threats to the Industry
Economic Uncertainty
Like many sectors, underground utility mapping can be affected by global economic shifts. Budget cuts in construction or public works can reduce demand for mapping services.
Data Privacy and Security
With utility data being stored and shared digitally, there are concerns about cybersecurity. Unauthorized access to utility maps can pose serious risks to public safety and national security.
Competition and Price Pressure
As the market grows, more companies are entering the space. This can lead to competitive pricing and reduced profit margins, especially for smaller service providers.
Dependence on Infrastructure Projects
The success of the utility mapping market is closely tied to infrastructure development. Any slowdown in construction activity can directly impact the industry’s growth.
Future Outlook: Underground Utility Mapping in 2032
Looking ahead to 2032, the underground utility mapping market is expected to be more connected, data-driven, and integrated than ever before. Key trends to watch include:
- Widespread use of AI and machine learning to analyze mapping data
- Real-time updates through mobile apps and cloud platforms
- Enhanced collaboration between public and private sectors
- Smart sensors that provide ongoing utility status monitoring
- Greater use of robotics and automation in utility detection
As smart city initiatives expand, accurate mapping of underground infrastructure will become a non-negotiable part of urban planning. Companies that innovate and adapt to new technologies will be best positioned to lead in this market.
Conclusion
The underground utility mapping market is entering a new era of innovation and demand. With strong growth drivers like smart city development, regulatory support, and technological advancements, the industry holds tremendous promise.
However, challenges such as high equipment costs, lack of skilled labor, and data accuracy must be addressed to unlock its full potential. By embracing modern tools, enhancing training, and promoting collaboration, stakeholders can ensure safer, smarter, and more efficient infrastructure development.
As we move toward 2032, underground utility mapping will be an essential tool for shaping the cities of tomorrow—reducing risks, improving safety, and powering smarter decisions for a connected world.