Caffeine is a widely consumed stimulant found in coffee, tea, and various beverages. Beyond its reputation for boosting energy and alertness, caffeine influences several physiological processes within the body, offering both immediate and long-term effects. Introduction to Caffeine’s Influence Caffeine is a natural stimulant that acts on the central nervous system, enhancing wakefulness and increasing
Caffeine is a widely consumed stimulant found in coffee, tea, and various beverages. Beyond its reputation for boosting energy and alertness, caffeine influences several physiological processes within the body, offering both immediate and long-term effects.
Introduction to Caffeine’s Influence
Caffeine is a natural stimulant that acts on the central nervous system, enhancing wakefulness and increasing alertness. It is prevalent in many everyday beverages and is consumed for its stimulating properties.
Immediate Effects: Energy and Alertness
Caffeine’s immediate impact is evident in the boost of energy and heightened alertness it provides. It achieves this by blocking adenosine receptors in the brain, preventing the neurotransmitter’s calming effects, thus promoting wakefulness.
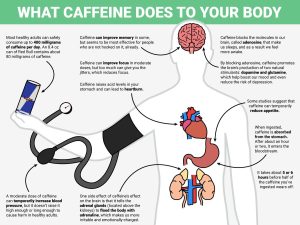
Image By: https://th.bing.com/
Beyond Energy: Broader Physiological Impacts
A. Metabolism and Fat Burning
Caffeine stimulates thermogenesis, which increases metabolic rate and may enhance fat burning. This has led to its inclusion in many weight-loss supplements, with research suggesting its potential role in weight management.
B. Physical Performance Enhancement
In addition to its effects on metabolism, caffeine can enhance physical performance. It increases adrenaline production, improving endurance, reducing perceived exertion, and enhancing overall performance during exercise.
C. Cognitive Function Beyond Alertness
Caffeine positively affects cognitive functions beyond alertness. It enhances focus, attention, memory, and various aspects of cognitive performance, promoting mental acuity.
D. Mood Regulation and Psychological Well-being
Beyond its cognitive effects, caffeine can influence mood and psychological well-being. It may improve mood, increase motivation, and alleviate symptoms of depression in some individuals.
Physiological Processes and Considerations
A. Digestive and Diuretic Effects
Caffeine’s impact on digestion and its diuretic properties can affect individuals differently. Some may experience gastrointestinal discomfort, while others may notice increased urination due to caffeine’s diuretic effects.
B. Bone Health and Calcium Absorption
High caffeine intake might interfere with calcium absorption, potentially affecting bone health. Research suggests a correlation between increased caffeine consumption and decreased bone density.
Individual Sensitivity and Tolerance
Individual responses to caffeine vary. Some individuals are more sensitive to its effects, while others develop tolerance over time, requiring larger doses to achieve the same effects.

Image By: https://www.positivehealthwellness.com/
Conclusion: Emphasizing Caffeine’s Broad Influence
In summary, caffeine’s influence extends beyond energy and alertness. Its impact spans various physiological processes, affecting metabolism, physical performance, cognition, mood, and potentially bone health. Understanding these effects can help individuals make informed choices about caffeine consumption.

















Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked with *