Diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels, affects millions of people worldwide. Managing diabetes effectively is crucial in preventing complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage. Over the years, diabetes management has evolved significantly, with new tools and treatments emerging to improve the quality of life for those affected.
Diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels, affects millions of people worldwide. Managing diabetes effectively is crucial in preventing complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage. Over the years, diabetes management has evolved significantly, with new tools and treatments emerging to improve the quality of life for those affected. This article explores the latest innovations in diabetes management, highlighting the advancements that are transforming the landscape of diabetes care.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems
One of the most significant innovations in diabetes management is the development of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems. Unlike traditional glucose meters that require finger-prick blood samples, CGM systems provide real-time glucose readings through a small sensor inserted under the skin. These systems offer several advantages:
- Real-Time Data: CGM systems continuously monitor glucose levels and provide real-time data, allowing individuals to make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and insulin dosing.
- Trend Analysis: CGM systems track glucose trends over time, helping users and healthcare providers identify patterns and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
- Alerts and Alarms: Many CGM systems come with customizable alerts and alarms that notify users of high or low glucose levels, reducing the risk of severe hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
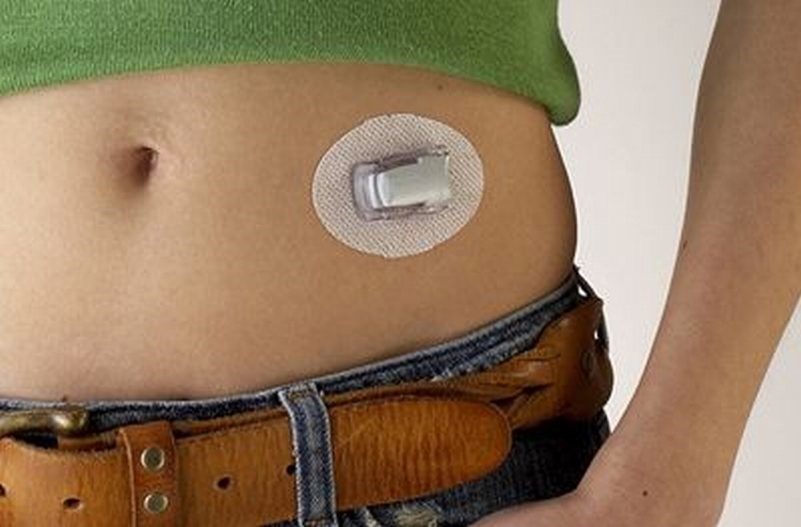
Artificial Pancreas Systems
The development of artificial pancreas systems represents a major breakthrough in diabetes management. These systems combine CGM technology with insulin pumps to create a closed-loop system that mimics the function of a healthy pancreas. The artificial pancreas automatically adjusts insulin delivery based on real-time glucose readings, reducing the burden of constant monitoring and manual insulin administration. This innovation has shown promise in improving glycemic control and reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Picture by: Yandex.com
Smart Insulin Pens
Smart insulin pens are another innovation that has revolutionized diabetes management. These devices are equipped with Bluetooth technology and can connect to smartphone apps, providing users with detailed information about their insulin doses. Some key features of smart insulin pens include:
- Dose Tracking: Smart insulin pens record the date, time, and amount of each insulin dose, helping users keep track of their insulin usage.
- Reminders: These pens can send reminders to users when it’s time to take their insulin, reducing the risk of missed doses.
- Data Sharing: Users can share their insulin data with healthcare providers, allowing for more personalized and effective treatment plans.
Picture by: Yandex.com
Advanced Insulin Formulations
Innovations in insulin formulations have led to the development of faster-acting and longer-lasting insulin types. These advanced formulations provide more flexibility in diabetes management and improve glycemic control. Some examples include:
- Ultra-Rapid-Acting Insulin: These insulins are designed to work faster than traditional rapid-acting insulins, allowing for more precise control of post-meal blood sugar spikes.
- Ultra-Long-Acting Insulin: These insulins provide a steady release of insulin over an extended period, reducing the need for multiple daily injections and improving overall blood sugar stability.
Non-Insulin Medications
In addition to insulin, several non-insulin medications have been developed to help manage diabetes. These medications work through different mechanisms to lower blood sugar levels and improve overall diabetes control. Some notable examples include:
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: These medications stimulate the release of insulin, slow down gastric emptying, and reduce appetite, leading to better blood sugar control and weight loss.
- SGLT2 Inhibitors: These drugs help the kidneys remove excess glucose from the bloodstream, lowering blood sugar levels and providing cardiovascular benefits.
- DPP-4 Inhibitors: These medications increase the levels of incretin hormones, which help regulate insulin production and glucose metabolism.
Digital Health Platforms
The rise of digital health platforms has also transformed diabetes management. These platforms offer a range of tools and resources to help individuals manage their condition more effectively. Some key features include:
- Telemedicine: Digital health platforms enable remote consultations with healthcare providers, making it easier for individuals to access medical advice and support.
- Mobile Apps: Numerous mobile apps are available to help users track their blood sugar levels, monitor their diet and exercise, and receive personalized recommendations.
- Online Communities: Digital health platforms often include online communities where individuals can connect with others who have diabetes, share experiences, and find support.
Personalized Medicine
Advancements in genetic research and precision medicine have paved the way for personalized diabetes management. By analyzing an individual’s genetic makeup, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans to better suit their needs. This approach can lead to more effective and targeted therapies, improving overall diabetes control and reducing the risk of complications.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are playing an increasingly important role in diabetes management. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict future outcomes. Some applications of AI and ML in diabetes care include:
- Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms can predict blood sugar fluctuations based on historical data, helping individuals and healthcare providers make proactive adjustments to treatment plans.
- Decision Support Systems: AI-powered decision support systems can provide personalized recommendations for insulin dosing, diet, and exercise, improving overall diabetes management.
- Automated Insulin Delivery: AI and ML technologies are being integrated into artificial pancreas systems to optimize insulin delivery and improve glycemic control.
Conclusion
The landscape of diabetes management is rapidly evolving, with new tools and treatments offering hope and improved quality of life for those affected by this chronic condition. Continuous Glucose Monitoring systems, artificial pancreas systems, smart insulin pens, advanced insulin formulations, non-insulin medications, digital health platforms, personalized medicine, and AI-powered technologies are all contributing to more effective and personalized diabetes care.
As these innovations continue to advance, individuals with diabetes can look forward to a future where managing their condition is less burdensome and more effective. By staying informed about the latest developments in diabetes management, individuals and healthcare providers can work together to achieve better outcomes and improve the overall well-being of those living with diabetes.