Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) systems have emerged as a revolutionary facet of modern healthcare, offering unparalleled benefits in patient care, data collection, and resource management. These systems leverage advanced technologies to monitor patients outside conventional clinical settings, thereby enhancing the quality of care while reducing healthcare costs. This article delves into the latest innovations in
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) systems have emerged as a revolutionary facet of modern healthcare, offering unparalleled benefits in patient care, data collection, and resource management. These systems leverage advanced technologies to monitor patients outside conventional clinical settings, thereby enhancing the quality of care while reducing healthcare costs. This article delves into the latest innovations in RPM systems, exploring how they are transforming the healthcare landscape.
The Evolution of Remote Patient Monitoring
The concept of RPM is not new; it has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, RPM systems were rudimentary, focusing primarily on telephonic communication and basic data transmission. However, the advent of digital health technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning, has ushered in a new era of sophisticated RPM systems.
Key Innovations in RPM Systems
1. Wearable Health Devices
Wearable health devices are at the forefront of RPM innovations. These devices, which include smartwatches, fitness trackers, and specialized medical wearables, continuously monitor vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. Companies like Apple, Fitbit, and Garmin have developed wearables that not only track physical activity but also provide insights into sleep patterns, stress levels, and overall health.
One notable innovation is the integration of electrocardiogram (ECG) capabilities into smartwatches. This feature allows for real-time monitoring of heart rhythms, enabling early detection of irregularities such as atrial fibrillation. Additionally, wearable devices equipped with photoplethysmography (PPG) sensors can detect changes in blood volume and oxygen saturation, providing critical data for managing chronic conditions like COPD and asthma.
2. IoT-Enabled Medical Devices
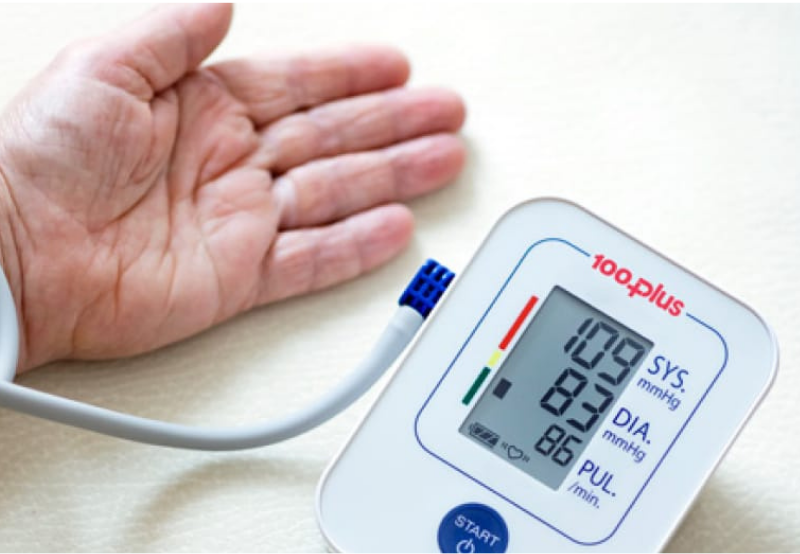
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized RPM by connecting various medical devices to a centralized system. IoT-enabled devices, such as glucometers, blood pressure monitors, and smart scales, automatically transmit data to healthcare providers in real-time. This seamless data flow facilitates continuous monitoring and timely interventions, reducing the need for frequent in-person visits.
For instance, IoT-enabled insulin pumps can adjust insulin delivery based on continuous glucose monitoring, optimizing diabetes management. Similarly, smart inhalers equipped with sensors can track medication usage and provide reminders, improving adherence to treatment plans for respiratory conditions.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming RPM systems by enabling predictive analytics and personalized care. These technologies analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential health issues before they become critical. For example, AI algorithms can analyze heart rate variability data from wearables to predict the onset of cardiac events, allowing for proactive interventions.
Machine learning models are also being used to develop personalized treatment plans. By analyzing patient data, including genetic information, lifestyle factors, and medical history, these models can recommend tailored interventions that optimize health outcomes. Furthermore, AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants are enhancing patient engagement by providing real-time support and answering health-related queries.
4. Telehealth Integration
The integration of telehealth with RPM systems has significantly expanded the scope of remote care. Telehealth platforms enable virtual consultations, allowing healthcare providers to assess patients’ conditions and adjust treatment plans remotely. This integration is particularly beneficial for managing chronic diseases, post-operative care, and mental health conditions.
For example, telehealth platforms integrated with RPM devices can provide a comprehensive view of a patient’s health status during virtual visits. Physicians can review real-time data from wearables and IoT-enabled devices, discuss symptoms with patients, and make informed decisions without the need for physical appointments. This approach not only enhances convenience but also reduces the risk of infection, particularly in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic.
5. Advanced Data Analytics
Data analytics plays a crucial role in leveraging the vast amounts of data generated by RPM systems. Advanced analytics tools can process and interpret this data, providing actionable insights for healthcare providers. Predictive analytics, for instance, can identify trends and potential health risks, enabling early interventions and preventive care.
Moreover, data analytics can help identify population health trends, informing public health strategies and resource allocation. By analyzing aggregated data from RPM systems, healthcare organizations can identify patterns related to disease outbreaks, medication adherence, and healthcare utilization, leading to more effective public health interventions.
Picture by: Yandex.com
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the numerous benefits, RPM systems face several challenges. Data privacy and security are paramount concerns, given the sensitive nature of health information. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures and compliance with regulations such as HIPAA is essential to protect patient data.
Another challenge is the integration of RPM systems with existing healthcare infrastructure. Interoperability between different devices and electronic health record (EHR) systems is crucial for seamless data exchange. Standardizing protocols and promoting collaboration among stakeholders can address these issues.
Looking ahead, the future of RPM systems is promising. Continued advancements in AI, IoT, and wearable technologies will further enhance the capabilities of these systems. The development of non-invasive monitoring techniques, such as remote imaging and biosensors, will expand the range of conditions that can be monitored remotely.
Moreover, the growing emphasis on patient-centered care will drive innovations that prioritize user experience and engagement. User-friendly interfaces, personalized health insights, and real-time feedback will empower patients to take an active role in managing their health.
Conclusion
Innovations in Remote Patient Monitoring systems are transforming healthcare by enabling continuous, real-time monitoring of patients outside traditional clinical settings. Wearable health devices, IoT-enabled medical devices, AI and machine learning, telehealth integration, and advanced data analytics are at the forefront of this revolution. These technologies not only enhance patient care but also improve resource management and reduce healthcare costs. While challenges such as data privacy and interoperability remain, the future of RPM systems is bright, promising a new era of personalized, proactive, and patient-centered healthcare.
















