Introduction Iodine, an unassuming trace element, holds a profound significance in our daily lives. Despite its often overlooked role, iodine is essential for maintaining our health. In this article, we will delve into the causes and potential health consequences of iodine deficiency, highlighting why addressing this nutritional concern is paramount for our overall well-being. Iodine
Introduction
Iodine, an unassuming trace element, holds a profound significance in our daily lives. Despite its often overlooked role, iodine is essential for maintaining our health. In this article, we will delve into the causes and potential health consequences of iodine deficiency, highlighting why addressing this nutritional concern is paramount for our overall well-being.
Iodine Deficiency: A Global Challenge
Iodine deficiency is a pervasive and persistent public health concern that affects populations worldwide. It stems from inadequate iodine intake, which can lead to a range of health issues. Let’s explore the causes of iodine deficiency and the potentially serious consequences it can have.
Causes of Iodine Deficiency
- Inadequate Dietary Intake: One of the primary causes of iodine deficiency is insufficient iodine in the diet. This often occurs in regions where iodine-rich foods, such as seafood, dairy, and iodized salt, are not readily available or consumed in limited quantities.
- Soil Depletion: The iodine content in the soil directly impacts the iodine content in crops and, consequently, the food we consume. In regions with iodine-deficient soil, the vegetables and grains grown there may also lack iodine.
Image By: https://www.birlahospital.com/
- Geographical Location: Geography plays a significant role in iodine deficiency. Areas located far from the coast, where seafood is less accessible, tend to have higher rates of deficiency. Additionally, mountainous regions with iodine-poor soil are particularly at risk.
- Lifestyle Choices: Dietary preferences can contribute to iodine deficiency. For example, individuals who follow strict vegetarian or vegan diets may have a lower iodine intake, as many iodine-rich foods are animal-based.
Consequences of Iodine Deficiency
Iodine deficiency can have far-reaching consequences for our health, affecting various aspects of our well-being:
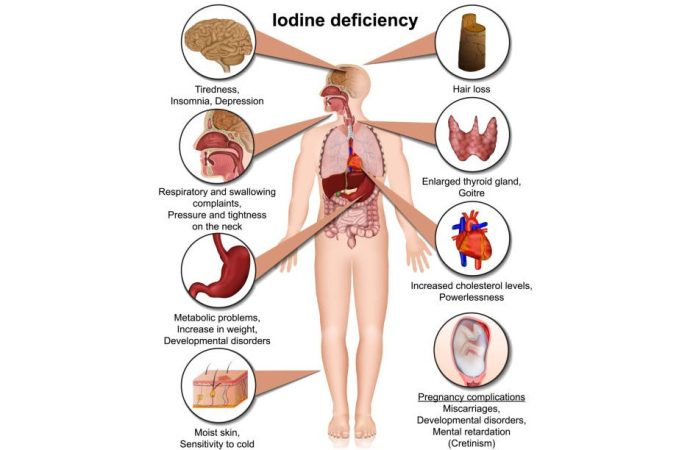
- Thyroid Dysfunction: The most well-known consequence of iodine deficiency is thyroid dysfunction. An underactive thyroid, known as hypothyroidism, can result in fatigue, weight gain, and sensitivity to cold. It can also lead to goiter, the visible enlargement of the thyroid gland.
- Cognitive Impairment: Iodine deficiency, especially during pregnancy and infancy, can lead to cognitive and developmental issues in children. This condition, known as cretinism, results in profound intellectual disabilities.
- Maternal Health: Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can have serious consequences for both the mother and the developing child. It can lead to stillbirths, preterm births, and intellectual disabilities in the offspring.
- Goiter: A visibly enlarged thyroid, or goiter, is a common consequence of iodine deficiency. While not typically painful, it can affect breathing and swallowing, and it serves as a visible reminder of the importance of iodine.
- Decreased Productivity: Iodine deficiency can affect productivity on a societal level. Cognitive impairment in affected individuals can result in decreased work capacity and economic productivity.
Addressing Iodine Deficiency
Addressing iodine deficiency is of paramount importance for individual and public health. Several strategies have proven effective in combatting this concern:
- Iodized Salt: The most widespread and accessible intervention is iodized salt. This simple solution has significantly reduced iodine deficiency in many regions.
- Dietary Diversification: Encouraging a diverse diet that includes iodine-rich foods like seafood, dairy, and eggs can be effective in addressing iodine deficiency.
- Supplementation: In regions where iodine deficiency remains a challenge, iodine supplementation programs may be necessary, particularly for pregnant women.
Image By: https://inside.hochdorf.com/
Conclusion
Iodine deficiency is a nutritional concern with wide-ranging consequences. Its causes include inadequate dietary intake, soil depletion, geographical location, and lifestyle choices. The potential health consequences range from thyroid dysfunction and cognitive impairment to maternal health issues and decreased productivity. To ensure our well-being and the health of future generations, addressing iodine deficiency through interventions like iodized salt, dietary diversification, and supplementation is paramount. Let us not underestimate the importance of this unassuming trace element and its profound impact on our health.

















Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked with *