Overview Hypokalemia and Its Effects, characterized by low blood potassium levels, is a medical condition with profound implications for bodily functions. This article aims to provide a thorough understanding of hypokalemia, exploring its impact on the body, identifying its causes, delving into symptoms, discussing diagnosis methods, and outlining effective treatment approaches. Additionally, preventive measures to
Overview
Hypokalemia and Its Effects, characterized by low blood potassium levels, is a medical condition with profound implications for bodily functions. This article aims to provide a thorough understanding of hypokalemia, exploring its impact on the body, identifying its causes, delving into symptoms, discussing diagnosis methods, and outlining effective treatment approaches. Additionally, preventive measures to mitigate the risk of hypokalemia will be discussed.
Symptoms and Causes
What is hypokalemia?
Potassium, an indispensable electrolyte, plays a vital role in the proper functioning of cells, muscles, and nerves. Hypokalemia is diagnosed when blood potassium levels fall below 3 mEq/L, signifying severe deficiency and potentially leading to adverse health outcomes such as abnormal heart rhythms and muscle weakness.
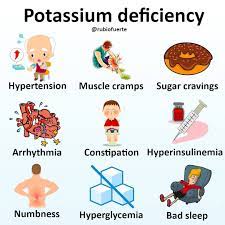
Image by: www.facebook.com
How does hypokalemia affect my body?
Insufficient potassium can disrupt essential bodily functions, resulting in abnormal heart rhythms, muscle weakness, and, in severe cases, paralysis. Understanding the repercussions of low potassium levels is crucial for recognizing and addressing symptoms promptly.
What causes hypokalemia?
Hypokalemia often stems from excessive potassium loss, primarily through vomiting, diarrhea, laxative use, and certain medications. Beyond these factors, underlying conditions such as adrenal disorders and rare genetic kidney disorders like Bartter’s syndrome may contribute to potassium imbalance.
What are the symptoms of hypokalemia?
Recognizing symptoms is pivotal for early intervention. While mild cases may be asymptomatic, common signs include constipation, palpitations, fatigue, and muscle weakness. In more severe cases, individuals may experience muscle twitches, cramps, paralysis, and abnormal heart rhythms.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is hypokalemia diagnosed?
Accurate diagnosis involves blood tests to measure potassium levels. Severe Hypokalemia and Its Effects is indicated when levels dip below 3 mEq/L. Additional tests, such as metabolic panels and electrocardiograms, help assess kidney function and detect abnormal heart rhythms associated with hypokalemia.

Image by: timesofindia.indiatimes.com
Management and Treatment
How is hypokalemia treated?
Treatment strategies vary based on the severity of hypokalemia. Mild cases often respond well to oral potassium supplements. In more severe instances, intravenous administration may be necessary, particularly when abnormal heart rhythms are present. Identifying and addressing the underlying cause is integral to effective management.
Prevention
How can I reduce my risk of hypokalemia?
Preventing hypokalemia involves adopting measures to maintain adequate potassium levels. Consider the following points:
- Balanced Diet: Maintain a diet rich in potassium by incorporating fruits, vegetables, lean meat, and fish.
- Hydration: Stay adequately hydrated to support electrolyte balance.
- Timely Medical Attention: Seek immediate medical care for prolonged vomiting or diarrhea, as these can lead to significant potassium loss.

Image by: www.verywellhealth.com
Outlook / Prognosis
What can I expect if I have hypokalemia?
Understanding the prognosis is essential for individuals with Hypokalemia and Its Effects. Mild cases typically respond well to oral supplements, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a potassium-rich diet. However, severe, untreated hypokalemia can lead to serious heart issues and paralysis, underscoring the critical need for prompt medical attention. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure ongoing monitoring and proper management.
Conclusion:
Hypokalemia demands a comprehensive approach, from recognizing symptoms and obtaining an accurate diagnosis to implementing effective treatment and preventive measures. With a focus on maintaining optimal potassium levels, individuals can actively collaborate with healthcare providers to navigate this condition and safeguard their overall well-being. Regular check-ups and adherence to prescribed treatments contribute to a positive outlook for those managing hypokalemia.

















Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked with *