In the past decade, the healthcare industry has undergone a significant transformation with the widespread adoption of Digital Health Records (DHRs). These electronic systems have revolutionized the way patient information is stored, accessed, and utilized, offering a plethora of advantages while also presenting certain challenges. This article delves into the growth of Digital Health Records,
In the past decade, the healthcare industry has undergone a significant transformation with the widespread adoption of Digital Health Records (DHRs). These electronic systems have revolutionized the way patient information is stored, accessed, and utilized, offering a plethora of advantages while also presenting certain challenges. This article delves into the growth of Digital Health Records, exploring their benefits and the obstacles they face.
The Rise of Digital Health Records
Digital Health Records, also known as Electronic Health Records (EHRs) or Electronic Medical Records (EMRs), have become a cornerstone of modern healthcare. Unlike traditional paper records, DHRs provide a comprehensive, real-time view of a patient’s medical history, facilitating better coordination and continuity of care. The shift towards digitalization has been driven by several factors, including technological advancements, policy initiatives, and the increasing demand for efficient healthcare services.
The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act of 2009 was a significant catalyst in the adoption of DHRs in the United States. The act provided financial incentives for healthcare providers to implement and meaningfully use EHR systems, leading to a surge in adoption rates. Today, the majority of healthcare facilities in developed nations have integrated some form of digital records into their operations.
Benefits of Digital Health Records
Improved Patient Care and Safety
One of the most significant benefits of Digital Health Records is the enhancement of patient care. DHRs enable healthcare providers to access a patient’s complete medical history, including past diagnoses, treatments, medications, and allergies. This comprehensive view helps in making informed decisions, reducing the risk of errors, and ensuring that patients receive appropriate and timely care.
Enhanced Coordination and Continuity of Care
Digital Health Records facilitate seamless communication and information sharing among healthcare providers. Whether a patient is visiting a primary care physician, a specialist, or a hospital, their medical information can be easily accessed and updated. This improved coordination reduces redundant tests and procedures, minimizes delays in treatment, and ensures continuity of care.
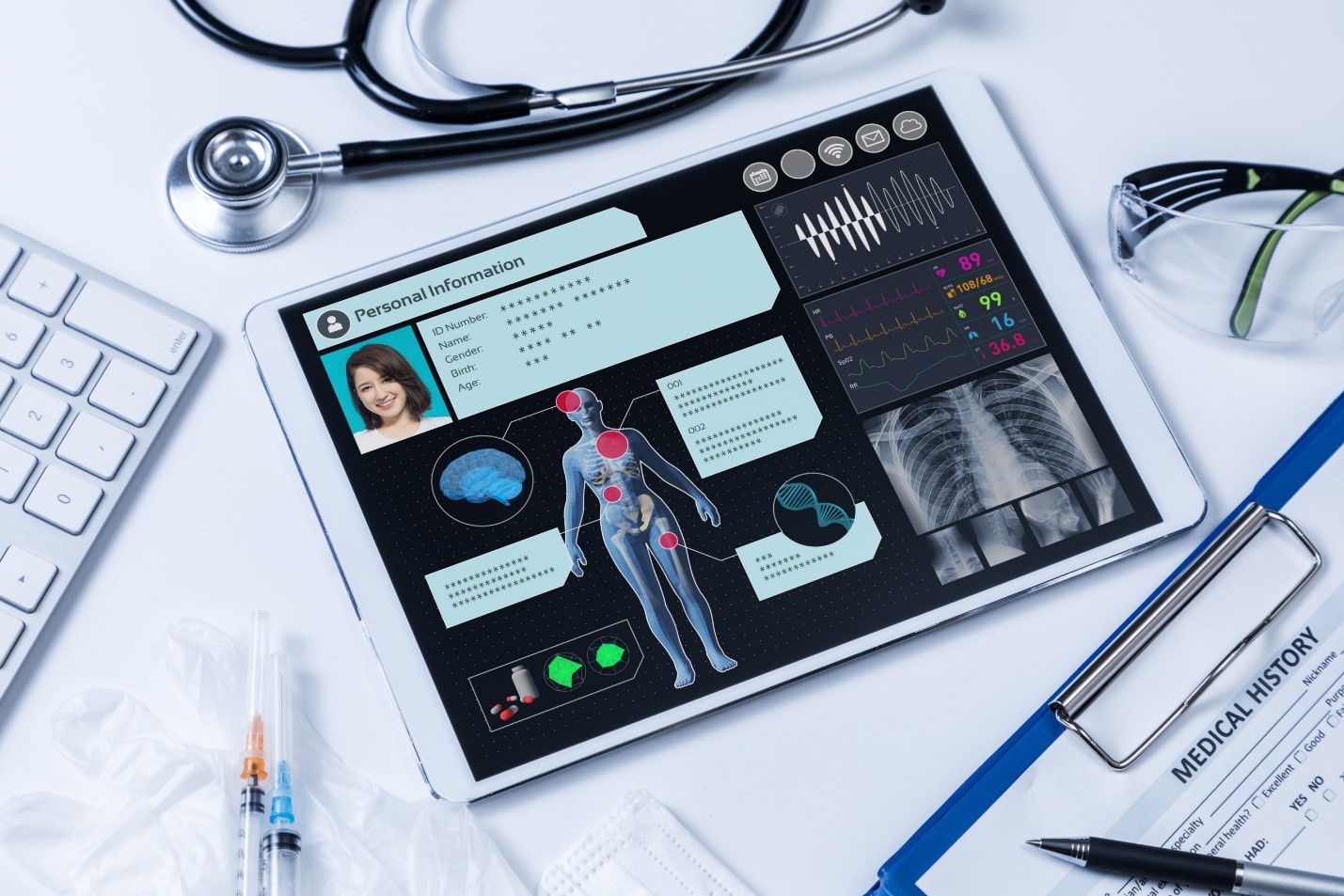
Picture by: Yandex.com
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
The transition from paper-based records to digital systems has streamlined administrative processes, leading to increased efficiency and productivity in healthcare settings. DHRs eliminate the need for manual record-keeping, reduce paperwork, and enable quick retrieval of patient information. This allows healthcare providers to spend more time on patient care and less on administrative tasks.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Digital Health Records generate a wealth of data that can be analyzed to gain insights into patient outcomes, treatment effectiveness, and population health trends. Healthcare organizations can leverage this data to identify patterns, improve clinical practices, and make evidence-based decisions. Additionally, DHRs support research efforts by providing a rich source of anonymized patient data for studies and clinical trials.
Patient Empowerment and Engagement
DHRs empower patients by giving them access to their own health information through patient portals. Patients can view their medical history, lab results, and treatment plans, and communicate with their healthcare providers. This transparency fosters patient engagement, encourages adherence to treatment plans, and promotes shared decision-making.
Challenges of Digital Health Records
Interoperability Issues
Despite the widespread adoption of Digital Health Records, interoperability remains a significant challenge. Different EHR systems often use proprietary formats and standards, making it difficult for them to communicate and exchange information seamlessly. This lack of interoperability can hinder the flow of information between healthcare providers and impact the quality of care.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
The digitization of health records has raised concerns about data security and patient privacy. Healthcare data is highly sensitive, and any breach can have severe consequences. Ensuring the security of DHRs requires robust encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Additionally, compliance with regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is essential to protect patient information.
High Implementation and Maintenance Costs
The implementation of Digital Health Records systems can be costly, particularly for smaller healthcare facilities with limited budgets. The initial investment includes the cost of hardware, software, training, and workflow redesign. Ongoing maintenance, system upgrades, and technical support also add to the financial burden. While the long-term benefits of DHRs are substantial, the upfront costs can be a barrier to adoption.
User Resistance and Training
The transition to Digital Health Records requires a significant change in the way healthcare providers operate. Some clinicians may resist adopting new technologies due to familiarity with paper-based systems or concerns about the usability of EHRs. Comprehensive training and ongoing support are crucial to ensure that healthcare providers can effectively use DHRs and realize their full potential.
Data Quality and Standardization
The accuracy and completeness of Digital Health Records are critical for delivering high-quality care. However, inconsistencies in data entry, variations in documentation practices, and lack of standardized terminologies can affect the quality of DHRs. Implementing standardized data entry protocols and conducting regular audits can help address these issues and improve the reliability of digital records.
Conclusion
The growth of Digital Health Records represents a monumental shift in the healthcare industry, offering numerous benefits that enhance patient care, improve efficiency, and support data-driven decision-making. However, the journey towards fully realizing the potential of DHRs is not without challenges. Interoperability issues, data security concerns, high implementation costs, user resistance, and data quality are some of the obstacles that need to be addressed.
As technology continues to evolve, efforts to overcome these challenges and optimize the use of Digital Health Records will be crucial. Collaboration among healthcare providers, policymakers, technology vendors, and patients is essential to create a seamless, secure, and efficient digital health ecosystem. By addressing these challenges and leveraging the benefits of DHRs, the healthcare industry can move closer to achieving the goal of providing high-quality, patient-centered care in the digital age.
















