Climate change is no longer a distant threat but a pressing reality with profound implications for public health. The intricate relationship between our planet’s changing climate and human health is becoming increasingly evident, necessitating urgent action and awareness. This article delves into the multifaceted ways in which climate change impacts public health, emphasizing the importance
Climate change is no longer a distant threat but a pressing reality with profound implications for public health. The intricate relationship between our planet’s changing climate and human health is becoming increasingly evident, necessitating urgent action and awareness. This article delves into the multifaceted ways in which climate change impacts public health, emphasizing the importance of understanding and addressing these challenges.
Rising Temperatures and Heat-Related Illnesses
One of the most direct effects of climate change is the increase in global temperatures. Prolonged heatwaves and higher average temperatures pose significant risks to human health, particularly for vulnerable populations such as the elderly, children, and those with preexisting health conditions. Heat-related illnesses, including heat exhaustion and heatstroke, are becoming more prevalent. Moreover, higher temperatures can exacerbate cardiovascular and respiratory conditions, leading to increased hospital admissions and mortality rates.
Air Quality and Respiratory Health
Climate change also affects air quality, with severe consequences for respiratory health. Rising temperatures and altered weather patterns contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and increase the concentration of particulate matter in the air. These pollutants can trigger asthma attacks, reduce lung function, and increase the incidence of respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Additionally, wildfires, which are becoming more frequent and intense due to climate change, release large amounts of smoke and pollutants, further degrading air quality and posing health risks.
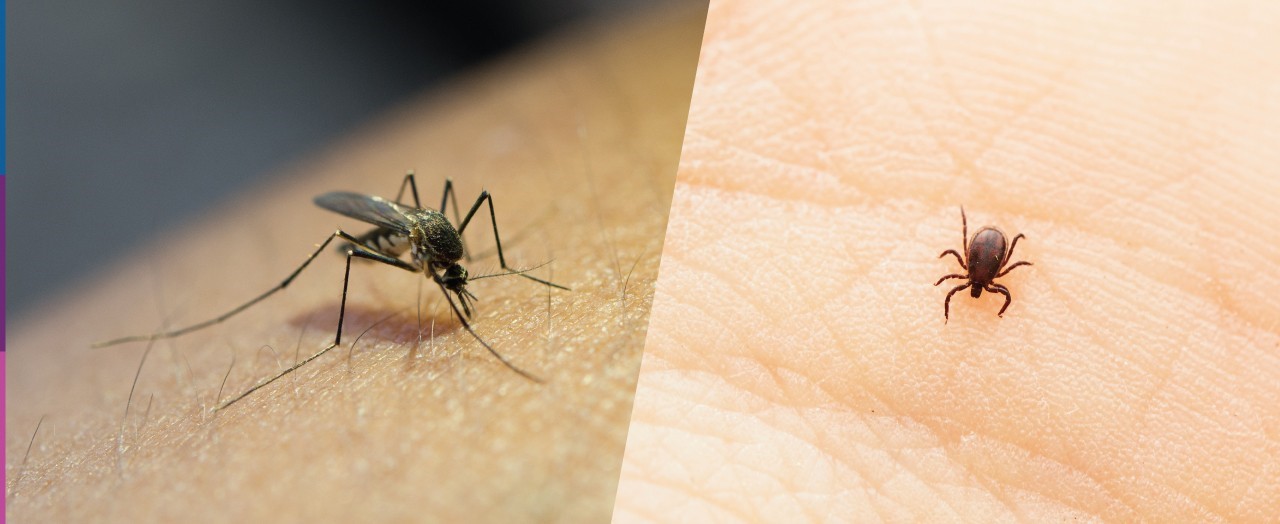
Vector-Borne Diseases
The changing climate influences the distribution and behavior of vectors such as mosquitoes and ticks, which can carry diseases like malaria, dengue fever, and Lyme disease. Warmer temperatures and altered precipitation patterns create more favorable conditions for these vectors to thrive and expand their range. As a result, regions previously unaffected by certain vector-borne diseases are now at risk, posing new public health challenges. Surveillance and control measures must adapt to these changes to prevent outbreaks and protect communities.
Picture by: Yandex.com
Water-Related Illnesses
Climate change impacts water quality and availability, leading to an increase in water-related illnesses. Extreme weather events, such as heavy rainfall and floods, can overwhelm water treatment systems, resulting in the contamination of drinking water with pathogens and chemicals. This contamination can cause outbreaks of diseases such as cholera, giardiasis, and cryptosporidiosis. Furthermore, rising sea levels and increased temperatures can promote the growth of harmful algal blooms, which produce toxins that contaminate water supplies and seafood, posing additional health risks.
Food Security and Nutrition
The effects of climate change on agriculture and food production have significant implications for public health. Changes in temperature, precipitation, and the frequency of extreme weather events can disrupt crop yields and reduce food availability. This can lead to food insecurity and malnutrition, particularly in vulnerable populations. Additionally, climate change can affect the nutritional quality of food, as elevated levels of carbon dioxide can reduce the concentration of essential nutrients in crops. Ensuring food security and adequate nutrition in the face of climate change is a critical public health priority.
Mental Health and Well-being
The psychological and emotional impacts of climate change are often overlooked but are equally important. The stress and anxiety associated with extreme weather events, displacement, and the uncertainty of future climate conditions can have profound effects on mental health. Communities affected by natural disasters such as hurricanes, floods, and wildfires may experience trauma, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Moreover, the existential threat posed by climate change can lead to feelings of helplessness and eco-anxiety, particularly among young people who are increasingly aware of the long-term implications.
Health Inequities and Vulnerable Populations
Climate change exacerbates existing health inequities, disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations. Low-income communities, indigenous peoples, and marginalized groups often have limited resources to adapt to climate-related health threats. These populations may lack access to healthcare, live in areas more susceptible to extreme weather events, and have fewer means to recover from climate-related disasters. Addressing these disparities is crucial to ensuring that public health interventions are equitable and inclusive.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
To mitigate the impact of climate change on public health, comprehensive strategies are needed. Mitigation efforts focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions to limit the extent of climate change. This includes transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable transportation and agriculture practices. Public health professionals can advocate for policies that reduce emissions and promote environmental sustainability.
Adaptation strategies are equally important, as they aim to reduce the vulnerability of communities to the health impacts of climate change. This includes improving infrastructure to withstand extreme weather events, enhancing surveillance and control of vector-borne diseases, and ensuring access to clean water and nutritious food. Public health systems must be strengthened to respond to the increasing demand for healthcare services related to climate change.
The Role of Public Health Professionals
Public health professionals play a crucial role in addressing the health impacts of climate change. They are at the forefront of research, education, and advocacy efforts to raise awareness about the links between climate change and health. By conducting epidemiological studies, public health researchers can identify emerging health threats and inform policy decisions. Education campaigns can help communities understand the risks and adopt protective behaviors. Advocacy efforts can influence policy changes at local, national, and global levels to prioritize climate action and public health.
Conclusion
The impact of climate change on public health is profound and multifaceted, affecting everything from heat-related illnesses and respiratory health to vector-borne diseases, water quality, food security, mental health, and health inequities. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that includes both mitigation and adaptation strategies. Public health professionals have a critical role to play in this effort, through research, education, and advocacy. By understanding and addressing the health impacts of climate change, we can protect vulnerable populations, reduce health disparities, and build resilient communities for the future.
















