The Rise of Smart Cities: Integrating Technology and Urban Living In the 21st century, urbanization is accelerating at an unprecedented rate. By 2050, it is estimated that nearly 70% of the global population will reside in urban areas. This rapid urbanization presents both opportunities and challenges, necessitating innovative solutions to ensure sustainable and efficient urban
The Rise of Smart Cities: Integrating Technology and Urban Living
In the 21st century, urbanization is accelerating at an unprecedented rate. By 2050, it is estimated that nearly 70% of the global population will reside in urban areas. This rapid urbanization presents both opportunities and challenges, necessitating innovative solutions to ensure sustainable and efficient urban living. Enter the concept of Smart Cities—urban areas that leverage technology to enhance the quality of life for their inhabitants. This article delves into the rise of smart cities, examining how technology is being integrated into urban living, the benefits it brings, and the challenges that lie ahead.
What is a Smart City?
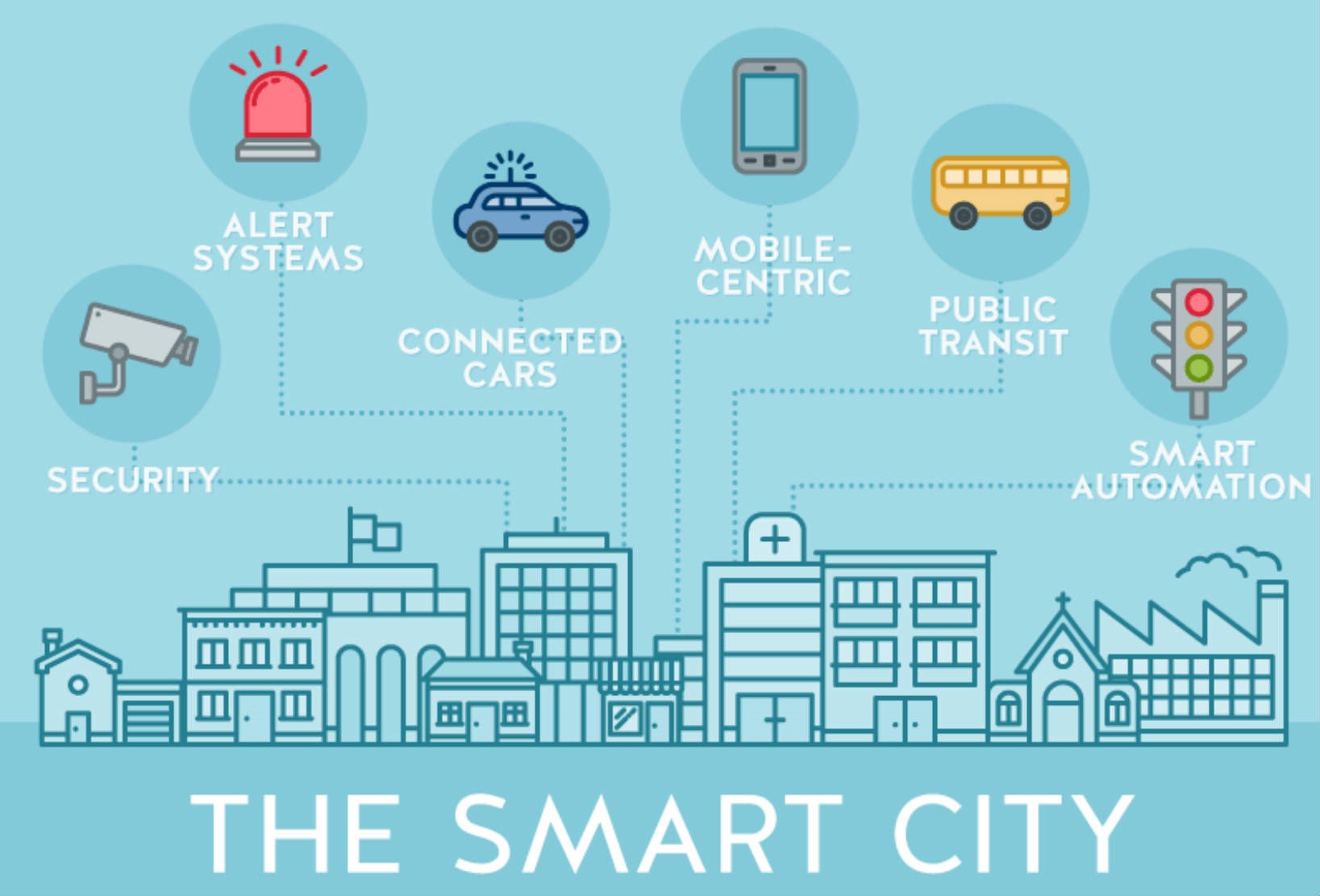
A smart city utilizes Information and Communication Technology (ICT) to improve operational efficiency, share information with the public, and provide a better quality of government services and citizen welfare. The core components of a smart city include:
- Smart Infrastructure: Integrating sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) devices into physical infrastructure to monitor and manage urban systems in real-time.
- Smart Governance: Utilizing data analytics and digital platforms to improve governance and citizen engagement.
- Smart Mobility: Enhancing transportation systems through technologies such as autonomous vehicles, smart traffic management, and shared mobility solutions.
- Smart Environment: Implementing sustainable practices through smart grids, renewable energy sources, and efficient waste management systems.
- Smart Living: Improving the quality of life through smart healthcare, education, and public safety initiatives.
The Integration of Technology in Urban Living
Smart Infrastructure
Smart infrastructure forms the backbone of a smart city. By embedding sensors and IoT devices into urban infrastructure, cities can collect and analyze data to optimize various services. For instance, smart grids can monitor electricity consumption in real-time, allowing for efficient energy distribution and reducing wastage. Similarly, smart water management systems can detect leaks and monitor water quality, ensuring a reliable supply of clean water.
Smart Governance
Smart governance involves the use of digital platforms and data analytics to enhance decision-making and public engagement. E-governance portals allow citizens to access government services online, reducing the need for physical visits and streamlining administrative processes. Additionally, open data initiatives enable citizens to access and analyze city data, fostering transparency and accountability.
Smart Mobility
Transportation is a critical aspect of urban living, and smart cities are leveraging technology to create more efficient and sustainable mobility solutions. Autonomous vehicles and connected car technologies are revolutionizing urban transportation by reducing traffic congestion and improving road safety. Smart traffic management systems use real-time data to optimize traffic flow, while shared mobility solutions such as bike-sharing and ride-hailing apps provide convenient and eco-friendly transportation options.
Picture by: Yandex.com
Smart Environment
Sustainability is a key focus of smart cities, and technology plays a crucial role in achieving environmental goals. Smart grids enable the integration of renewable energy sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Waste management systems equipped with IoT sensors can monitor waste levels and optimize collection routes, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. Additionally, air quality monitoring systems provide real-time data on pollution levels, enabling cities to take proactive measures to improve air quality.
Smart Living
Smart living initiatives aim to enhance the quality of life for urban residents. Telemedicine platforms enable remote healthcare consultations, improving access to medical services. Smart education solutions such as online learning platforms and digital classrooms provide flexible and personalized learning experiences. Public safety initiatives leverage technologies such as surveillance cameras and emergency response systems to ensure the safety and security of citizens.
Benefits of Smart Cities
The integration of technology into urban living offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Efficiency: Smart cities optimize the use of resources, reducing wastage and operational costs. For example, smart grids and water management systems ensure efficient energy and water distribution.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Smart living initiatives improve access to healthcare, education, and public services, enhancing the overall quality of life for urban residents.
- Sustainability: Smart cities promote sustainable practices through the use of renewable energy sources, efficient waste management, and air quality monitoring, reducing the environmental impact of urbanization.
- Economic Growth: The development of smart cities creates new economic opportunities, attracting investment and fostering innovation. The technology sector, in particular, benefits from the increased demand for smart city solutions.
- Safety and Security: Public safety initiatives such as surveillance systems and emergency response platforms enhance the safety and security of urban residents.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the numerous benefits, the development of smart cities also presents several challenges and considerations:
- Data Privacy and Security: The extensive use of data in smart cities raises concerns about data privacy and security. Ensuring the protection of sensitive information and preventing cyber-attacks is crucial.
- Digital Divide: The reliance on technology in smart cities may exacerbate the digital divide, leaving behind those without access to digital tools and services. Ensuring inclusivity and accessibility is essential.
- Infrastructure Costs: The development and maintenance of smart infrastructure require significant investment. Securing funding and managing costs can be challenging for city authorities.
- Interoperability: Integrating various technologies and systems within a smart city requires interoperability. Ensuring that different systems can communicate and work together seamlessly is vital.
- Regulatory and Ethical Considerations: The implementation of smart city initiatives must adhere to regulatory and ethical standards. Addressing concerns related to surveillance, data usage, and citizen rights is essential.
Conclusion
The rise of smart cities represents a transformative shift in urban living, leveraging technology to create more efficient, sustainable, and livable urban environments. By integrating smart infrastructure, governance, mobility, environment, and living solutions, smart cities can address the challenges of rapid urbanization and improve the quality of life for their residents. However, the development of smart cities also requires careful consideration of data privacy, inclusivity, infrastructure costs, interoperability, and regulatory standards. As cities around the world continue to embrace smart technologies, the future of urban living holds immense potential for innovation and progress.
















