Introduction Diabetes, a chronic health condition affecting millions globally, demands a comprehensive understanding. In this exploration, we unravel the complexities of diabetes, its impact on the body, management strategies, and the crucial role lifestyle choices play in preventing and controlling this prevalent ailment. Understanding Diabetes At its core, diabetes is a chronic condition influencing how
Introduction
Diabetes, a chronic health condition affecting millions globally, demands a comprehensive understanding. In this exploration, we unravel the complexities of diabetes, its impact on the body, management strategies, and the crucial role lifestyle choices play in preventing and controlling this prevalent ailment.
Understanding Diabetes
At its core, diabetes is a chronic condition influencing how the body processes food into energy. The body typically breaks down consumed food into sugar (glucose), releasing it into the bloodstream. The pancreas responds to elevated blood sugar levels by releasing insulin, acting as a key to enable cells to use glucose as an energy source.
However, in the case of diabetes, this harmonious process is disrupted. Either the body doesn’t produce sufficient insulin, or the produced insulin is ineffective. Consequently, excess blood sugar remains in the bloodstream, fostering severe health problems such as heart disease, vision impairment, and kidney disease over time.

Image by: www.endocrinologyadvisor.com
Management Strategies
While there is no cure for diabetes, adopting a proactive approach through lifestyle changes significantly mitigates its impact. Weight management, a balanced diet, and regular physical activity play pivotal roles in diabetes management. Beyond these fundamental pillars, adhering to prescribed medications, seeking diabetes education and support, and maintaining regular healthcare appointments contribute to a comprehensive management plan.
Diabetes by the Numbers
The statistical landscape of diabetes in the United States underscores its magnitude and impact on public health:
- Approximately 38 million US adults grapple with diabetes, with a concerning 1 in 5 individuals unaware of their diabetic status.
- Diabetes ranks as the eighth leading cause of death in the United States.
- It stands as the primary cause of kidney failure, lower-limb amputations, and adult blindness.
- The last two decades witnessed a staggering doubling in the number of adults diagnosed with diabetes.
These statistics emphasize the urgent need for increased awareness, preventive measures, and effective management strategies to curb the rising tide of diabetes-related complications.
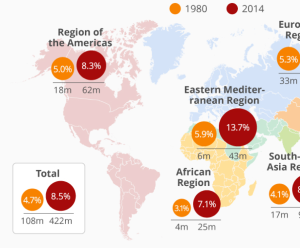
Image by: yendex.com
Types of Diabetes: A Diverse Spectrum
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Type 1 diabetes, accounting for 5-10% of all diabetes cases, is primarily caused by an autoimmune reaction where the body mistakenly attacks itself, halting insulin production.
- This form can manifest at any age, and its onset is often rapid. Daily insulin administration becomes a lifeline for individuals with type 1 diabetes.
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Representing the majority (90-95%) of diabetes cases, type 2 diabetes occurs when the body fails to use insulin efficiently, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
- Developing over several years, type 2 diabetes is traditionally associated with adults but is increasingly diagnosed in children, teenagers, and young adults.
- Lifestyle changes, including weight management, healthy eating habits, and regular exercise, serve as effective preventive measures against type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational Diabetes
- Gestational diabetes affects pregnant women who have not previously experienced diabetes.
- While typically temporary, gestational diabetes poses risks to both mother and baby during pregnancy and increases the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes later in life for the mother.

Image by: yendex.com
Prediabetes: A Silent Precursor
Prediabetes, a precursor to type 2 diabetes, afflicts over 98 million adults in the United States, with a staggering 8 in 10 individuals unaware of their condition. Characterized by elevated blood sugar levels not yet meeting the criteria for a type 2 diabetes diagnosis, prediabetes serves as a critical warning sign.
Individuals with prediabetes face increased risks of developing type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. The silver lining lies in the availability of CDC-recognized lifestyle change programs that empower individuals to take proactive steps, reversing prediabetes and steering towards a healthier trajectory.
Image by: yendex.com
Comparative Table: A Comprehensive Overview
| Diabetes Type | Cause | Percentage of Cases | Treatment | Onset Age |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 Diabetes | Autoimmune reaction | 5-10% | Daily insulin | Any age |
| Type 2 Diabetes | Insulin inefficiency | 90-95% | Lifestyle changes | Typically adults |
| Gestational Diabetes | Pregnancy-related | – | Monitoring and lifestyle | During pregnancy |
| Prediabetes | Elevated blood sugar levels | – | Lifestyle changes | Typically adults |
This comprehensive table distills key information about each type of diabetes, aiding in a clearer understanding of their distinctions and respective management strategies. Treatment for other health problem
Conclusion
In conclusion, diabetes presents a multifaceted challenge, demanding a holistic approach to understanding, prevention, and management. Armed with knowledge about the diverse types of diabetes, the importance of lifestyle choices, and the prevalence of prediabetes, individuals can proactively navigate this health landscape.
It is imperative to foster awareness, encourage routine screenings, and promote lifestyle modifications to curb the escalating diabetes epidemic. By embracing a proactive stance, individuals can take charge of their health, reducing the impact of diabetes-related complications and enhancing overall well-being. In the pursuit of a healthier future, education, awareness, and informed lifestyle choices emerge as the linchpins of effective diabetes management.
















