What is Walking Pneumonia? Walking pneumonia, medically known as atypical pneumonia, is a milder form of pneumonia that typically doesn’t require bed rest or hospitalization for most individuals. Unlike typical pneumonia, which is often caused by bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae, walking pneumonia is commonly caused by bacteria called Mycoplasma pneumoniae or other pathogens like viruses
What is Walking Pneumonia?
Walking pneumonia, medically known as atypical pneumonia, is a milder form of pneumonia that typically doesn’t require bed rest or hospitalization for most individuals. Unlike typical pneumonia, which is often caused by bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae, walking pneumonia is commonly caused by bacteria called Mycoplasma pneumoniae or other pathogens like viruses or fungi. Explore More About Health Problems And Their Solutions ( POTS Syndrome)
Symptoms of Walking Pneumonia
Subtle Signs
Walking pneumonia is characterized by mild symptoms that can often be mistaken for a common cold or bronchitis. These symptoms may include:
- Persistent cough, often dry or with minimal phlegm
- Low-grade fever
- Fatigue or weakness
- Sore throat
- Headache
Gradual Onset
One notable aspect of walking pneumonia is its gradual onset. Symptoms may develop over several days, and individuals may not initially realize the severity of their condition.
Respiratory Distress
While walking pneumonia is generally mild, it can lead to respiratory distress in some cases, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions. Symptoms such as shortness of breath or chest pain may indicate a need for medical attention.
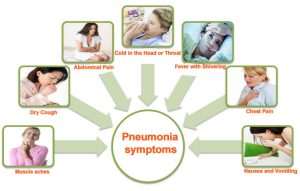
Image by: yendex.com
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnostic Methods
Diagnosing walking pneumonia often involves a combination of clinical evaluation, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Healthcare providers may listen to the lungs with a stethoscope to detect abnormal sounds indicative of pneumonia. Additionally, chest X-rays and laboratory tests, such as sputum cultures or blood tests, may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for walking pneumonia typically involves antibiotics if the condition is bacterial in origin. However, if the cause is viral, antibiotics may not be effective. Rest, adequate hydration, and over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms such as fever or cough may also be recommended. It’s essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve, to prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
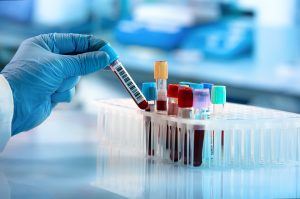
Image by: yendex.com
Prevention Strategies
Hand Hygiene
Practicing good hand hygiene, including regular handwashing with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizers, can help prevent the spread of respiratory infections like walking pneumonia.
Avoiding Close Contact
Avoiding close contact with individuals who have respiratory infections, especially if they are coughing or sneezing, can reduce the risk of exposure to pathogens that cause walking pneumonia.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including getting adequate sleep, eating a balanced diet, staying physically active, and managing stress, can support a robust immune system, making individuals less susceptible to respiratory infections.
Vaccination
While there isn’t a specific vaccine, staying up to date on recommended vaccinations, such as the pneumococcal vaccine and the influenza vaccine, can help prevent certain types of pneumonia and reduce the overall burden of respiratory illnesses.
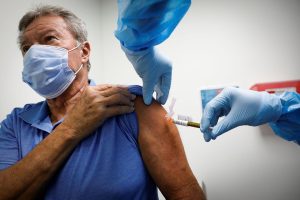
Image by: yendex.com
| Aspect | Typical Pneumonia | Walking Pneumonia |
|---|---|---|
| Severity | Can be severe, may require hospitalization | Generally mild, often manageable at home |
| Causative Agents | Primarily bacterial, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae | Often caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae, viruses, or fungi |
| Symptoms | Sudden onset, high fever, productive cough | Gradual onset, mild symptoms resembling a cold or bronchitis |
| Treatment | Antibiotics often necessary | Antibiotics may or may not be required, rest and symptom management usually suffice |
Conclusion
Walking pneumonia may be less severe than typical pneumonia, but it still requires attention and appropriate management to prevent complications and ensure a speedy recovery. Recognizing the symptoms, seeking timely medical care, and following recommended prevention strategies are essential steps in managing this respiratory condition effectively.
Remember, while this article provides valuable insights, it’s crucial to consult healthcare professionals for personalized medical advice and treatment. By staying informed and taking proactive measures, individuals can safeguard their respiratory health and well-being.
















