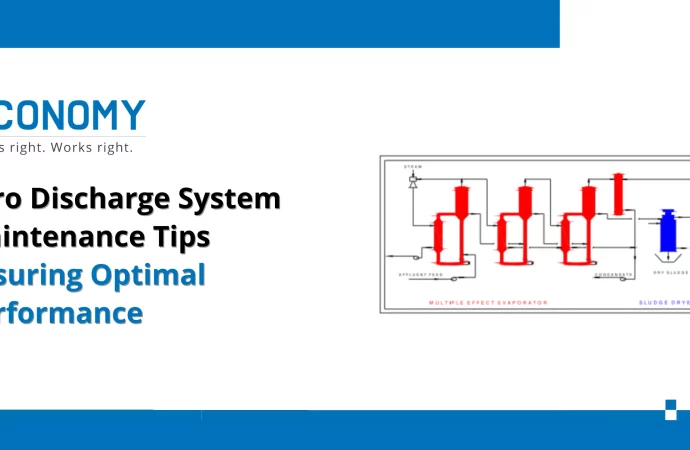
Introduction Zero Discharge Systems (ZDS) have become an integral part of modern industries, particularly in sectors like textiles, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemicals, where wastewater treatment is critical. The system ensures that no liquid effluent is discharged into the environment by recovering, recycling, and reusing treated water. While this technology supports sustainability and regulatory compliance,
Introduction
Zero Discharge Systems (ZDS) have become an integral part of modern industries, particularly in sectors like textiles, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemicals, where wastewater treatment is critical. The system ensures that no liquid effluent is discharged into the environment by recovering, recycling, and reusing treated water. While this technology supports sustainability and regulatory compliance, its efficiency largely depends on consistent maintenance. Proper upkeep not only prolongs equipment life but also guarantees stable performance and cost-effectiveness.
Why Regular Upkeep is Essential for Zero Discharge System?
Regular Zero Discharge System maintenance is critical because these systems involve complex processes, including ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis (RO), evaporation, and crystallization. Each stage has sensitive components that, if neglected, can fail and affect the entire process.
- Prevents Costly Breakdowns: Timely upkeep avoids unexpected failures that can halt production.
- Ensures Compliance: Environmental regulations demand strict adherence. Poor maintenance could result in non-compliance penalties.
- Improves Efficiency: Well-maintained systems operate with higher energy efficiency and reduced chemical usage.
- Extends Lifespan: Regular cleaning, inspections, and timely replacement of parts protect capital-intensive equipment.
- Sustainability: Proper functioning ensures industries meet their sustainability goals by achieving true zero liquid discharge.
Key Maintenance Tips for Zero Discharge Systems
- Routine Inspection of Filters and Membranes: RO and ultrafiltration membranes are prone to fouling and scaling. Regular cleaning with suitable chemicals and monitoring for pressure drops ensures optimal flow and efficiency.
- Descaling and Cleaning of Evaporators: Evaporators handle high concentrations of salts and solids. Regular descaling and cleaning help prevent scaling, which can drastically reduce heat transfer efficiency.
- Monitoring pH and TDS Levels: Continuous monitoring of pH, hardness, and Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) levels in influent water avoids unnecessary stress on the system and improves recycling efficiency.
- Lubrication and Mechanical Care: Pumps, agitators, and motors need periodic lubrication, alignment checks, and vibration monitoring to prevent breakdowns.
- Checking Automation Controls: Zero discharge systems often integrate advanced automation. Regular calibration of sensors and inspection of control panels help avoid misoperation.
- Sludge Handling and Disposal: Proper handling and timely disposal of sludge from crystallizers or evaporators prevent clogging, environmental hazards, and efficiency loss.
Answers for Normal Issues
Like any industrial setup, Zero Discharge Systems face recurring issues. Here are some common challenges and their solutions:
1. Scaling in RO Membranes
Solution: Use antiscalants, ensure proper pre-treatment, and schedule chemical cleaning based on system performance data.
2. High Energy Consumption in Evaporators
Solution: Insulate heat exchangers, optimize operating parameters, and clean heat transfer surfaces regularly.
3. Pump Failures
Solution: Maintain proper lubrication schedules, monitor vibration levels, and replace worn-out bearings or seals promptly.
4. Automation Errors
Solution: Conduct frequent calibration of sensors, maintain updated software backups, and train staff on troubleshooting.
5. Fouling in Crystallizers
Solution: Monitor feed water quality, use antifoaming agents, and perform periodic cleaning with approved chemicals.
Best Practices for Feasible Support
- Implement Preventive Maintenance (PM): Instead of waiting for a breakdown, schedule periodic checks and preventive tasks for membranes, pumps, and electrical systems.
- Maintain Detailed Logs: Recording operating pressures, flow rates, and energy consumption helps identify early warning signs of problems.
- Training for Operators: Skilled and trained personnel are essential for correct operation, troubleshooting, and safety.
- Use of Genuine Spare Parts: Always replace membranes, gaskets, and mechanical parts with certified spares to ensure compatibility and reliability.
- Energy Optimization: Run systems at recommended load levels to avoid stress on equipment and unnecessary energy consumption.
Devices and Assets for Upkeep
To ensure smooth functioning, industries should invest in the right maintenance tools and assets:
- Online Monitoring Systems: Real-time sensors for flow, pH, TDS, and pressure allow immediate detection of irregularities.
- Vibration Analyzers: For rotating machinery, vibration analyzers help in early detection of mechanical issues.
- Chemical Cleaning Systems: Automated CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems simplify membrane and pipeline cleaning.
- Spare Parts Inventory: Maintaining an in-house stock of critical spare parts reduces downtime during unexpected failures.
- Diagnostic Software: Advanced software helps monitor efficiency trends and predict maintenance needs.
Guaranteeing Ideal Execution Through Customary Support
Achieving optimal performance from a Zero Discharge System requires a structured maintenance culture:
- Scheduled Maintenance Calendar: Develop a calendar-based schedule for inspections, cleaning, and replacements.
- Regular Performance Audits: Conduct monthly or quarterly audits to benchmark system efficiency and identify gaps.
- Third-Party Service Support: Partnering with specialized service providers ensures expert oversight, especially for complex equipment like crystallizers and multiple-effect evaporators.
- Safety Integration: Maintenance activities should always incorporate safety practices to protect operators and prevent accidents.
- Continuous Improvement: Feedback from audits and operations should be used to refine processes, reduce energy costs, and enhance water recovery rates.
Conclusion
Zero Discharge Systems are vital for industries striving to meet environmental regulations while achieving sustainable operations. However, their complexity demands systematic upkeep. From regular membrane cleaning to sludge management, preventive maintenance plays a decisive role in ensuring uninterrupted performance. With the right practices, tools, and expertise, industries can not only maintain compliance but also extend the life of their systems and reduce operating costs. Ultimately, consistent maintenance ensures that Zero Discharge Systems deliver on their promise of efficiency, reliability, and sustainability.