Introduction Ringworm, despite its name, is not caused by a worm but rather by a fungal infection. It is a common condition that affects the skin, scalp, and nails, causing discomfort and sometimes embarrassment. Understanding how to identify and control ringworm is essential for maintaining good health and hygiene. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve
Introduction
Ringworm, despite its name, is not caused by a worm but rather by a fungal infection. It is a common condition that affects the skin, scalp, and nails, causing discomfort and sometimes embarrassment. Understanding how to identify and control ringworm is essential for maintaining good health and hygiene. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the details of ringworm, offering expert advice on its identification and effective control measures.
Understanding Ringworm: What is it?
Ringworm, medically known as dermatophytosis, is a contagious fungal infection that can affect the skin, scalp, and nails. Contrary to popular belief, it is not caused by worms but by various fungi known as dermatophytes. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments and can spread through direct contact with an infected person, animal, or object.
Types of Ringworm
There are several types of ringworm, each affecting different parts of the body:
1. Tinea Corporis (Body Ringworm)
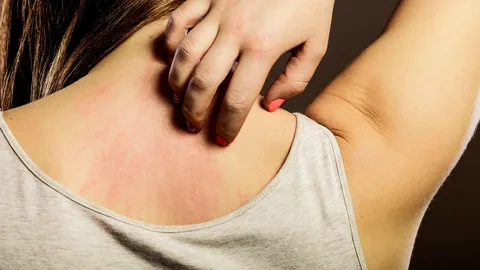
This type of ringworm affects the skin on the body, causing red, scaly patches that may itch or burn. It is commonly transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual or by sharing contaminated items such as clothing or towels.
2. Tinea Capitis (Scalp Ringworm)
Scalp ringworm primarily affects the scalp and hair follicles, leading to hair loss and the formation of scaly, inflamed patches on the scalp. It is most common in children and can spread through contact with contaminated combs, brushes, or hats.
3. Tinea Pedis (Athlete’s Foot)
Athlete’s foot is a type of ringworm that affects the feet, particularly the spaces between the toes. It causes itching, burning, and flaking of the skin, often accompanied by redness and inflammation. Athlete’s foot thrives in warm, moist environments such as locker rooms and swimming pools.
4. Tinea Cruris (Jock Itch)
Jock itch affects the groin and inner thighs, causing red, itchy rashes that can spread to the buttocks and genital area. It is more common in men and is often associated with sweating and friction in the groin area.

Image by: yendex.com
Identifying Ringworm: Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of ringworm is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Here are some common indicators to watch out for:
- Circular Rash: Ringworm often presents as a red, circular rash with raised edges and a clear center. The affected area may be scaly, inflamed, or blistered.
- Itching and Discomfort: Ringworm can cause intense itching, burning, or stinging sensations, leading to discomfort and irritation.
- Hair Loss: In cases of scalp ringworm, hair loss and bald patches may occur, accompanied by scaly or crusty lesions on the scalp.
- Nail Changes: Nail ringworm, or onychomycosis, can cause thickening, discoloration, and brittleness of the nails, leading to pain and discomfort. Explore More About (Tourette Syndrome)
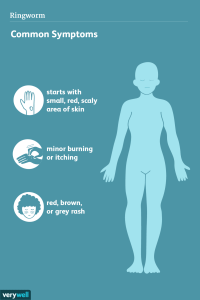
Image by: yendex.com
Controlling Ringworm: Prevention and Treatment
Effective control of ringworm involves a combination of prevention strategies and targeted treatments. Here’s what you can do to prevent ringworm:
Prevention
1. Practice Good Hygiene
- Regular Handwashing: Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water, especially after using the bathroom, touching animals, or participating in activities that may expose you to fungi.
- Keep Skin Dry: Dry your skin thoroughly after bathing or swimming, paying particular attention to areas prone to sweating, such as the groin, armpits, and feet.
2. Avoid Sharing Personal Items
- Clothing and Towels: Avoid sharing clothing, towels, or personal items with others, especially if they have a known fungal infection.
- Athletic Gear: Use separate towels, socks, and athletic gear to prevent the spread of athlete’s foot and jock itch in communal areas such as gyms and locker rooms.
Treatment
1. Topical Antifungal Medications
- Over-the-Counter Options: Many cases of ringworm can be treated with over-the-counter antifungal creams, lotions, or powders. These products typically contain ingredients such as clotrimazole, miconazole, or terbinafine.
- Prescription Medications: In severe or persistent cases, your healthcare provider may prescribe stronger antifungal medications, such as oral tablets or prescription-strength creams.
2. Home Remedies
- Tea Tree Oil: Applying diluted tea tree oil to the affected area may help alleviate symptoms and inhibit the growth of fungi.
- Garlic: Some people believe that garlic has antifungal properties and may help treat ringworm when applied topically.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Soaking the affected area in diluted apple cider vinegar may help relieve itching and inflammation associated with ringworm.

Image by: yendex.com
Conclusion
Ringworm is a common fungal infection that can affect the skin, scalp, and nails, causing discomfort and irritation. By understanding the signs and symptoms of ringworm and implementing effective prevention and treatment strategies, you can effectively control this condition and maintain good skin health. If you suspect you have ringworm or are experiencing persistent symptoms, consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.