Introduction: As an experienced economist and writer, I’ve observed the profound effects of globalization on local economies around the world. This article delves into the multifaceted impact of globalization, examining both the opportunities and challenges it presents. From economic growth and job creation to sustainability and cultural identity, we’ll explore how local economies navigate the
Introduction:
As an experienced economist and writer, I’ve observed the profound effects of globalization on local economies around the world. This article delves into the multifaceted impact of globalization, examining both the opportunities and challenges it presents. From economic growth and job creation to sustainability and cultural identity, we’ll explore how local economies navigate the complexities of an increasingly interconnected world.
1. Understanding Globalization
Before examining its impact, it’s essential to define globalization. This section provides an overview of globalization, highlighting the increased interconnectedness of economies, cultures, and technologies across borders.
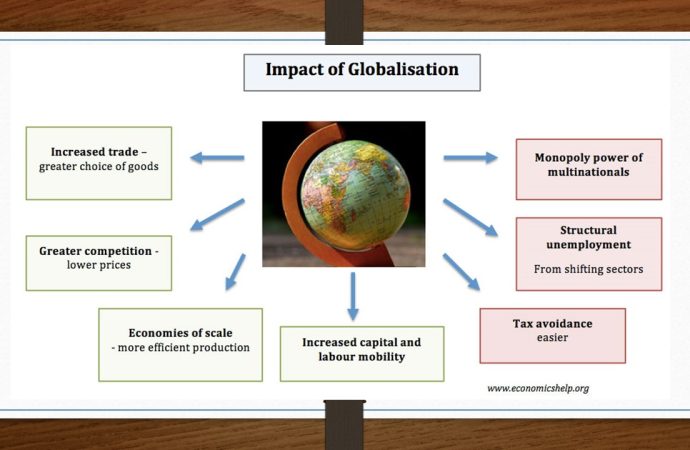
2. Economic Growth and Development

Image by : Yandex
Globalization often leads to economic growth and development by providing access to larger markets, foreign investments, and advanced technologies. This section discusses how local economies benefit from these opportunities and the role of multinational corporations in driving growth.
3. Job Creation and Employment Patterns
The expansion of global trade and investment can create jobs and transform employment patterns. Learn about the sectors most affected by globalization, the types of jobs created, and the implications for local labor markets.
4. Challenges to Local Industries
While globalization offers growth opportunities, it also poses challenges to local industries. This section explores the competitive pressures local businesses face from international companies and the strategies they can employ to remain competitive.
5. Cultural Identity and Homogenization
Globalization can lead to cultural homogenization, where local cultures are influenced or overshadowed by dominant global cultures. Discuss the impact of globalization on cultural identity, the preservation of local traditions, and the emergence of a global culture.
6. Environmental Sustainability
The increased economic activity resulting from globalization has significant environmental implications. Examine the environmental challenges posed by globalization, such as increased resource consumption and pollution, and the measures needed to promote sustainable practices.
7. Income Inequality and Social Disparities
Globalization can exacerbate income inequality and social disparities within and between countries. This section highlights the factors contributing to inequality, the effects on local communities, and potential solutions to address these disparities.
8. Global Supply Chains and Local Economies
Global supply chains connect local economies to international markets. Learn about the benefits and risks of global supply chains, including their impact on local businesses, employment, and economic resilience.
9. Policy Responses and Local Adaptation
Governments play a crucial role in managing the impact of globalization on local economies. Explore the policy responses that can help mitigate the negative effects and maximize the benefits of globalization, such as trade regulations, education, and infrastructure development.
10. The Future of Globalization and Local Economies

Image by : Yandex
What does the future hold for globalization and local economies? This concluding section provides a forward-looking perspective on emerging trends, potential disruptions, and the ways local economies can adapt to an evolving global landscape.
Informative Table: Key Impacts of Globalization on Local Economies
| Impact | Description | Examples |
| Economic Growth | Access to larger markets and investments | Expansion of export-oriented industries |
| Job Creation | New employment opportunities in various sectors | Growth in technology and service industries |
| Competitive Pressures | Increased competition from international companies | Local businesses adapting to global standards |
| Cultural Homogenization | Influence of global cultures on local traditions | Spread of global brands and media |
| Environmental Impact | Increased resource consumption and pollution | Need for sustainable practices |
| Income Inequality | Widening gap between rich and poor | Disparities in wealth distribution |
| Supply Chain Connectivity | Integration into global supply networks | Local production for global markets |
Comparative Table: Pre-Globalization vs. Post-Globalization Economies
| Aspect | Pre-Globalization Economies | Post-Globalization Economies |
| Market Access | Limited to local and regional markets | Access to global markets and consumers |
| Foreign Investment | Minimal foreign investment | Significant foreign direct investment (FDI) |
| Employment Opportunities | Limited job variety, agriculture dominant | Diverse job opportunities, growth in services |
| Cultural Influence | Predominantly local cultural practices | Increased influence of global cultures |
| Environmental Practices | Traditional, low-impact practices | Modern practices with higher environmental impact |
| Income Distribution | More equitable but limited resources | Increased inequality with wealth concentration |
Conclusion: Navigating the Globalized Future
Globalization presents both opportunities and challenges for local economies. By understanding its multifaceted impact, local communities, businesses, and governments can develop strategies to harness the benefits while mitigating the drawbacks. As we move forward, fostering sustainable practices, preserving cultural identities, and addressing inequality will be crucial in ensuring that globalization contributes to a more prosperous and equitable world.