Introduction Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a prevalent, long-term condition affecting approximately 12 million people in the UK. This gastrointestinal disorder manifests with symptoms such as abdominal pain and altered bowel movements, significantly impacting the daily lives of those affected. While medical interventions are available, the diverse nature of IBS necessitates a multifaceted, individualized approach
Introduction
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a prevalent, long-term condition affecting approximately 12 million people in the UK. This gastrointestinal disorder manifests with symptoms such as abdominal pain and altered bowel movements, significantly impacting the daily lives of those affected. While medical interventions are available, the diverse nature of IBS necessitates a multifaceted, individualized approach to treatment. In this comprehensive article, we explore non-medication strategies and lifestyle adjustments that individuals with IBS can incorporate into their daily lives to manage symptoms effectively.

Image by: https://www.bbcgoodfood.com/howto/guide/balanced-diet-women
Understanding the Complexity of IBS
IBS is a complex condition, and its precise causes remain unknown. Consequently, finding a singular medication that universally addresses the underlying issues is challenging. This reality underscores the importance of embracing self-care strategies tailored to the unique needs of each individual.
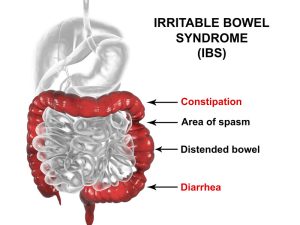
Image by: https://drmagaziner.com/colon-and-bowel/irritable-bowel-syndrome-why-some-sufferers-do-not-see-treatment-results/
Dietary Focus: A Personalized Approach
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing IBS symptoms. Dr. Simon Smale, a renowned consultant gastroenterologist, advocates for a dietary approach that involves regular meals and the avoidance of excess caffeine, alcohol, and fizzy drinks. Acknowledging the individuality of triggers, maintaining a food and symptom diary can help identify patterns.
The Low-FODMAP Diet: Targeting Triggers
One prominent dietary strategy gaining attention in the IBS community is the low-FODMAP diet. FODMAPs (Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols) are hard-to-digest carbohydrates that may contribute to IBS symptoms. By temporarily eliminating and then systematically reintroducing high-FODMAP foods, individuals can pinpoint specific triggers and customize their diets accordingly.
Managing Stress: A Psychological Dimension
Stress, whether chronic or acute, is a significant contributor to IBS symptoms. The relationship between stress and IBS is not entirely clear, but many individuals with IBS also contend with psychological conditions like generalized anxiety disorder. Behavioral therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, hypnosis, and yoga, have demonstrated benefits comparable to the low-FODMAP diet in managing IBS symptoms.
Additional Strategies for Holistic Management
Beyond diet and stress management, alternative therapies and herbal remedies offer additional avenues for relief. Peppermint oil, for instance, has shown efficacy in alleviating IBS symptoms. Regular exercise, besides promoting overall well-being, can expedite intestinal transit and help alleviate constipation. For those on the go, maintaining accessibility with tools like the Radar NKS Key ensures access to over 9,000 disabled-accessible toilets in the UK.

Image by: https://charlestongi.com/news&events/the-low-fodmap-diet-for-irritable-bowel-syndrome/
The Role of Probiotics: Nurturing Gut Health
Studies suggest that probiotic supplements can play a role in treating IBS by balancing intestinal flora. However, this is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The effectiveness of probiotics varies among individuals due to differences in microbiomes and genetics. Finding the right probiotic may require some trial and error.
Embracing a Personalized Journey
In the quest to manage IBS without medication, individuals, in collaboration with their medical practitioners, embark on a personalized journey. Recognizing that there is no universal solution, this journey often involves a process of trial and error. Over time, most individuals with IBS gain insights into their triggers, facilitating an improvement in their condition.
Conclusion
How to treat IBS without medication | Patient is a multifaceted endeavor that encompasses dietary adjustments, stress management, and personalized strategies. By actively participating in their care through these non-medication approaches, individuals with IBS can take control of their symptoms and enhance their overall quality of life. This comprehensive approach empowers individuals to navigate the challenges of IBS with resilience and adaptability.





















Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked with *